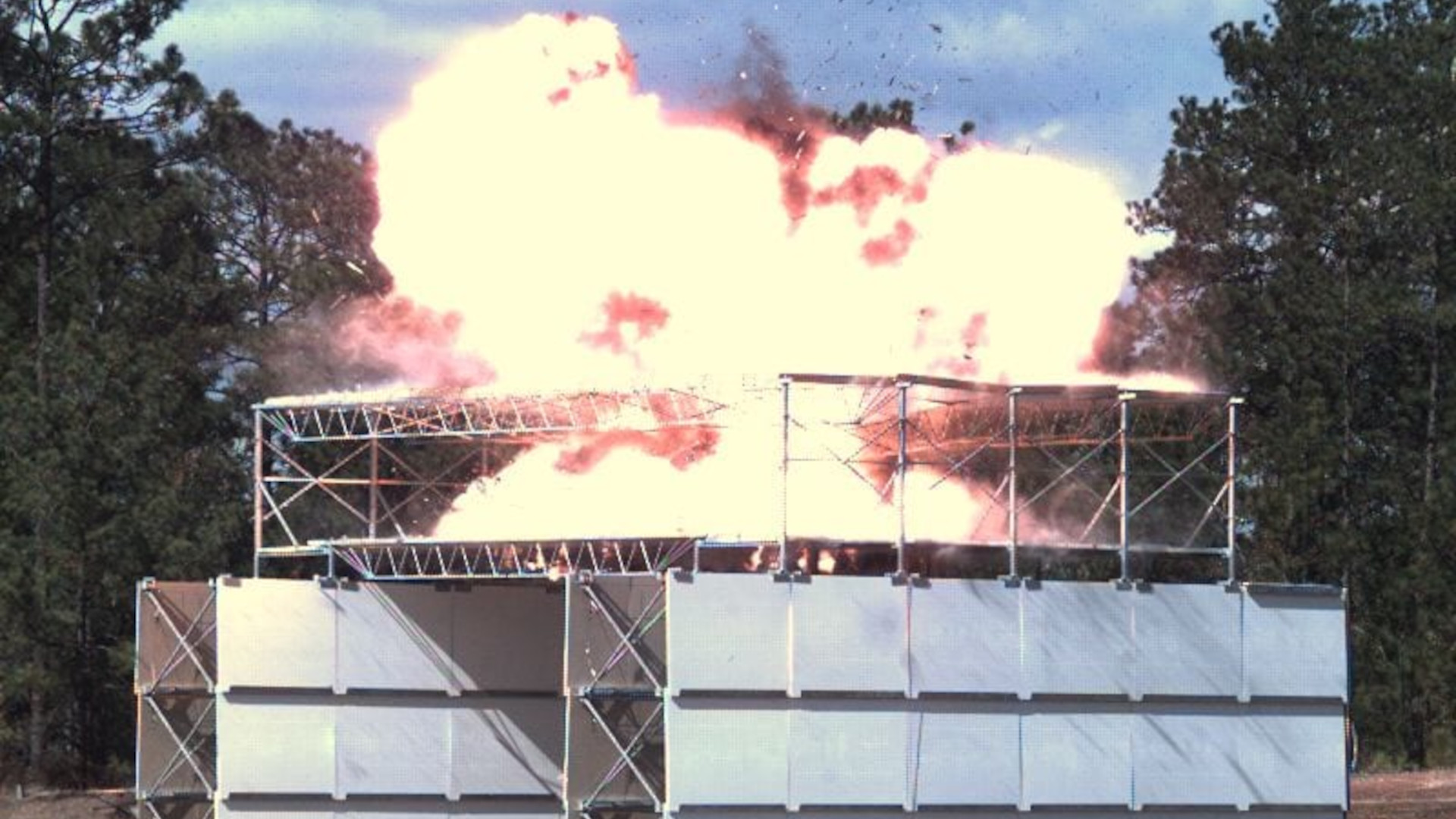
New Pentagon guidance for defending critical infrastructure against drone attacks calls for the increased use of netting, cables, and other kinds of passive physical defenses. This reflects a notable shift in policy within the department. For years now, U.S. military officials have often pushed back on the utility and cost-effectiveness of investing more in the physical hardening of bases and other critical facilities, especially shelters to shield aircraft from drones and other threats.
The Joint Inter-Agency Task Force 401 (JIATF-401) released the three-page document on “Physical Protection of Critical Infrastructure” last Friday. The Pentagon established JIATF-401 last August to coordinate counter-drone efforts across the department and help accelerate the fielding of new capabilities. Last week, the Pentagon also announced new authorities for military base commanders, expanding their options for responding to drone threats more broadly.
The new guidance from JIATF-401 talks about “critical infrastructure” mostly in terms of civilian sites ranging from power plants to sports venues. Drones do present real and still growing threats to critical civilian infrastructure, something TWZ has been calling attention to for years now. The Pentagon explicitly said the document had been released as part of work it has been doing in cooperation with the White House’s FIFA Task Force, which is preparing for the United States to host the World Cup later this year. However, it is made clear that the contents are equally applicable to helping protect military facilities from uncrewed aerial systems.
“When we talk about Homeland defense, we’re not just talking about military bases, power grids and ports; we’re talking about places where Americans gather. With major international events like the World Cup on the horizon, the security of our stadiums, for example, is a national priority,” U.S. Army Brig. Gen. Matt Ross, Director of JIATF-401, said in a statement accompanying the release. “Whether it’s a forward operating base, an outdoor concert venue or a stadium hosting the World Cup, the principles of risk assessment and physical protection outlined in this guide remain the same. This new guidance provides a common playbook for our forces to work closely with federal and local partners to ensure a safe and secure environment against the growing challenge of nefarious drones.”
The new counter-drone guidance’s central concept is a framework called HOP, standing for Harden, Obscure, Perimeter.
“Hardening does not mean enclosing an entire facility, but selectively introducing obstacles that disrupt predictable aerial access,” the document explains. “Even modest obstacles can deter low-cost, consumer-grade drones and force higher-risk flight profiles.”
As noted, the guidance highlights nets and tensioned cables as examples of this kind of cost-effective hardening. It also recommends closing retractable roofs and otherwise covering any other roof openings where and when it is feasible to do so. Underscoring the immediate focus on the World Cup, the document notes that “netting used to protect fans from projectiles can be repurposed to disrupt sUAS [small uncrewed aerial systems] flight and observation.”

The guidance also recommends the construction of more substantial “permanent or semi-permanent structural shielding, including concrete walls, enclosures, or hardened roofs designed to protect critical systems from overhead approach, observation, or objects released from a UAS.”
We will come back to all of this in a moment.
The “Obscure” component of the HOP framework focuses on making it harder for drones and their operators to find their targets in the first place. This can include an array of different tactics, techniques, and procedures, such as physical camouflage and decoys, as well as regular changes to how personnel and assets move through a facility. “If a drone cannot easily identify targets, crowds, or critical systems, its effectiveness drops sharply,” the new guidance notes.

Lastly, there is the “Perimeter” portion of the HOP framework, which is centered on expanded security zones around a specific site and ways to improve general situational awareness. “Pushing the effective perimeter outward forces drones to operate at greater distance, which strains battery life, degrades video and control links, increases the chance of operator exposure, [and] creates a larger safety buffer if a drone is downed.”

As an aside, the recently announced new counter-drone authorities for the commanders of U.S. military bases include the ability to respond to threats inside expanded zones beyond the facility’s immediate “fence-line.” The right-sizing of perimeters around domestic facilities and their enforcement has been a particularly complex issue for the U.S. government when it comes to counter-drone policies in recent years. Potential second-order impacts to surrounding areas, especially in densely populated urban environments, have to be taken into account and mitigated. This all imposes limits on the kind of assets that can be employed to neutralize drone threats once they’ve been detected, as you can read more about here.

As mentioned, the “Harden” part of the HOP frame stands out given how U.S. military officials have treated the topic in the past, at least publicly.
“We will have the need for bases, the main operating bases from which we operate,” U.S. Air Force Gen. Kevin Schneider, head of Pacific Air Forces (PACAF), said during a panel at the Air & Space Forces Association’s (AFA) 2025 Warfare Symposium last March. “The challenge becomes, at some point, we will need to move to austere locations. We will need to disaggregate the force. We will need to operate out of other locations, again, one for survivability, and two, again, to provide response options.”
Schneider added at that time that his service was faced with the need to “make internal trades” in how to apply available funding, including “do we put that dollar towards, you know, fixing the infrastructure at Kadena [Air Base in Japan] or do we put that dollar towards restoring an airfield at Tinian.”

“I got tons of airfields from tons of allies, and we have access to all of them. The problem is, I can only protect a few of them,” now-retired Air Force Gen. James Hecker, then head of U.S. Air Forces in Europe (USAFE), another member of that same panel, had also said. “We can’t have that layered [defensive] effect for thousands of airbases. There’s just no way it’s going to happen.”
“I’m not a big fan of hardening infrastructure,” Gen. Kenneth Wilsbach, then head of PACAF, had also said at a media roundtable at the Air & Space Forces Association’s main annual symposium back in 2023. “The reason is because of the advent of precision-guided weapons… you saw what we did to the Iraqi Air Force and their hardened aircraft shelters. They’re not so hard when you put a 2,000-pound bomb right through the roof.”
It is worth noting here that traditional high-end guided missiles and other precision-guided munitions are no longer necesarily required to carry out strikes of this kind. Drones costing thousands of dollars, and able to be launched from very long distances away, can now execute precision attacks.
Wilsbach is now Chief of Staff of the Air Force, the service’s top officer.
The U.S. military has faced pushback from Congress on the topic of hardening. Multiple independent assessments have also raised alarms. TWZ has been following this often-heated debate closely.
There have been signs that the U.S. military’s position on hardening, and that of the Air Force’s more specifically, has been shifting already. In 2024, authorities at Langley Air Force Base in Virginia and Seymour Johnson Air Force Base in North Carolina both put out contracting notices asking for information about nets and other physical barriers to stop potential drone attacks. Langley had become a focal point for the drone threat discussion by that point after the base was subjected to weeks of still largely unexplained drone incursions in December 2023, which we were first to report.

Last year, the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers (USACE) announced that it had developed upgrades for a family of modular, rapidly deployable protective structures specifically to improve their effectiveness against drone attacks.

“The technology is not going to solve this problem for us. We can’t field a system that will stop every drone,” JIATF-401 director Gen. Ross told TWZ and other outlets during a press call in December in response to a direct question about physical hardening from this author. “At the end of that would be protection, which would be netting or fencing or physical barriers that would prevent a [sic] unmanned system from having its intended effect.”
Gen. Ross had said that this was among the things JIATF-401 had discussed in meetings with the FBI and other law enforcement agencies as part of World Cup preparations, presaging the release of the new guidance last week.
“As you think about protection, I would go all the way down to protective protection type assets, those will be included in our marketplace. And so if somebody wants to buy a $10,000 radar that has limited range, they’ll be able to buy it on the marketplace. If they want to buy a low cost interceptor for … [small drones] that just uses kinetic energy to defeat a drone – that’s a drone that hits a drone for $1,000 – they’ll be able to buy it on our marketplace,” he added. “If they want to buy physical barrier material, whether it’s a fishing net or a chain link fence, they’ll also be able to buy that as part of that counter-UAS marketplace.”
The central “marketplace” mentioned here, through which elements of the military and other U.S. government agencies can source counter-drone capabilities, is a key initiative that JIATF-401 has been working on and that you can learn more about here.
It is important to stress that U.S. military officials are unified in their position that there is no one-size-fits-all approach to countering drones. Physical hardening is just one part of a layered approach and is not a ‘silver bullet’ solution to protect against all types of drone threats. Active defenses, including electronic warfare jammers, drone-like interceptors like Gen. Ross mentioned, and more traditional anti-aircraft assets, are still part of the equation, to differing degrees, for defending against drones at home and abroad.

At the same time, the ongoing conflict in Ukraine has shown that even limited, lower-cost measures like netting can be useful for disrupting attacks by smaller kamikaze drones and loitering munitions in the ongoing conflict in Ukraine.
Last year, near-simultaneous covert attacks by Ukrainian forces on multiple air bases in Russia utilizing quadcopter-type kamikaze drones underscored the level of damage that even lower-tier uncrewed aerial attackers can inflict on high-value targets. Mass drone attacks are only set to get more threatening as time goes on, as the barrier to entry on automated targeting and swarming capabilities lowers thanks to the steady proliferation of artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies. This, in turn, only increases the challenges for defenders, including the prospect of simply being overwhelmed. For years, TWZ has been separately sounding the alarm on how aircraft sitting on open flightlines are especially vulnerable, in general.
Outside of the United States, among adversaries and allies alike, there has also been a growing trend toward more physical hardening at air bases and other facilities. China has embarked on a particularly extensive effort to build new hardened and unhardened shelters at air bases across the country. The Chinese have been observed building other kinds of hardened infrastructure, including a new pattern of protected air defense sites along their disputed border with India, as well. Even before the unprecedented drone attacks last year, Russia had also been working to add new shelters, hardened and unhardened, to various air bases, but with a focus on ones closer to the fighting in Ukraine.

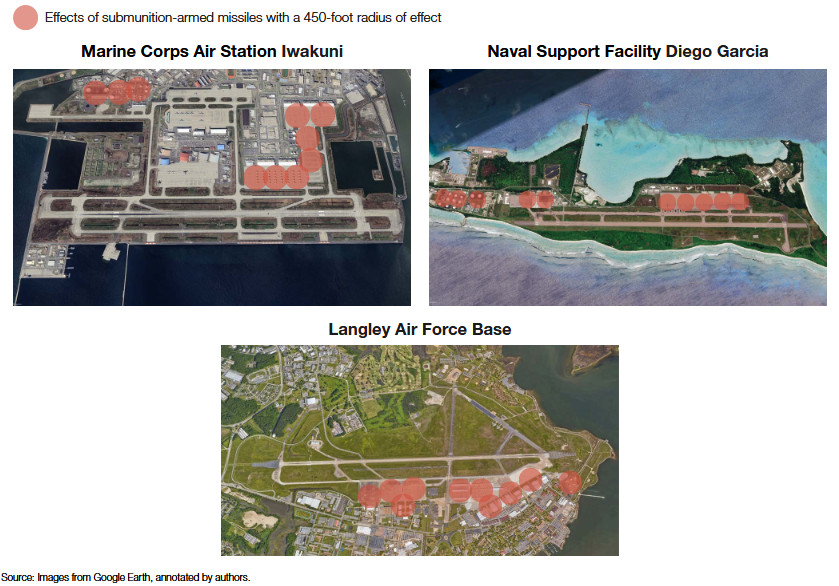
Structures that are sturdy enough even just to protect against shrapnel could have broader value, too. Just over a year ago, the Hudson Institute think tank in Washington, D.C., published a report assessing that 10 missiles with warheads capable of scattering cluster munitions across an area with a 450-foot diameter could be enough to neutralize all exposed aircraft on the ground and critical fuel storage at various key airbases. Marine Corps Air Station Iwakuni in Japan and Naval Support Facility Diego Garcia in the Indian Ocean, as well as Langley in Virginia, were specifically highlighted, as seen below.
Overall, the Pentagon’s counter-drone prescriptions are still evolving, especially when it comes to defending bases and critical civilian infrastructure within the United States. At the same time, despite public stances that officials have taken in the past, hardened structures and other kinds of physical defenses have become an important part of the current counter-drone playbook.
Contact the author: joe@twz.com