Royal Canadian Air Force (RCAF) Maj. Gen. Chris McKenna spends a good part of his days and nights figuring how to counter the growing threats China and Russia pose to the high north. Cruise missiles, launched from enemy aircraft well into international airspace, count among his biggest concerns.
McKenna serves as commander of 1 Canadian Air Division, operational commander for the Canadian North American Aerospace Defense Command (NORAD) Region (CANR) and the Canadian Joint Forces Air Component Commander. As such, he helps oversee an ambitious, $4 billion project to build a new Over the Horizon Radar system designed to sense threats almost 2,000 miles away. He also has many other responsibilities, like preparing for the integration of F-35 stealth fighters into the RCAF.
In a recent, exclusive hour-long interview, McKenna offered details about the radar development program, the mysterious 2023 shoot-down incident over the Yukon, and his biggest worries as Russia and China increase their individual military capabilities and frequently operate jointly.
You can catch up with the first part of that interview here.

Some of the questions and answers have been slightly edited for clarity.
Q: How confident are you that NORAD can protect the Arctic domain, and what are the biggest threats emanating from this area?
A: That’s a great question, and it starts with the adversary. From my point of view, the acute threat is Russia; from a NORAD point of view, historically, that has been the threat that we have postured ourselves against. But the emerging or pacing threat is certainly China and what they are doing.
And a great example of that is last summer, we had a combined bomber patrol that threatened North America. So you had a Chinese H-6K bomber paired with and bouncing through Russian infrastructure in the north, in the Russian Arctic, and they conducted a run at the Alaska Air Defense Identification Zone (ADIZ). So we met those bombers, both Canada and the U.S., together. U.S. F-35s and F-16s, my F-18s were postured and met them when they entered the ADIZ and escorted them out. But it’s very interesting to see the collusion between two adversaries in a way that is very different from what we’ve seen in the past.
Q: What are your biggest concerns?
A: I worry about ballistic missile threats, which continue and persist. Hypersonics as an emerging threat. But the ones that I really worry about are cruise missiles. So air-launched cruise missiles emanating from bombers, and we’re watching Russian bombers shoot those same weapons that we’re concerned about every single day into Ukraine. So we know they work, and we know what their ranges are, and they’re significant.

And I worry about sea-launched cruise missiles in the maritime domain. And what advanced submarines can do in terms of holding North America at risk.
Q: What are the biggest challenges to protecting the Arctic domain, and what has to change from what exists now?
A: In the 1990s, there was a large recapitalization of the radar line in the Arctic North known as the North Warning System, and it fuses Canada and the U.S. We essentially have coastal radars around Alaska and then down the western seaboard of North America. We have radars that go along the north side of the Arctic landmass onto Baffin Island and wrap around Quebec and Newfoundland all the way down to Maine. So we have sort of a radar fence that goes around.
We have 52 total Canadian radars that are up in the north. But they are co-owned. The U.S. co-funds them.
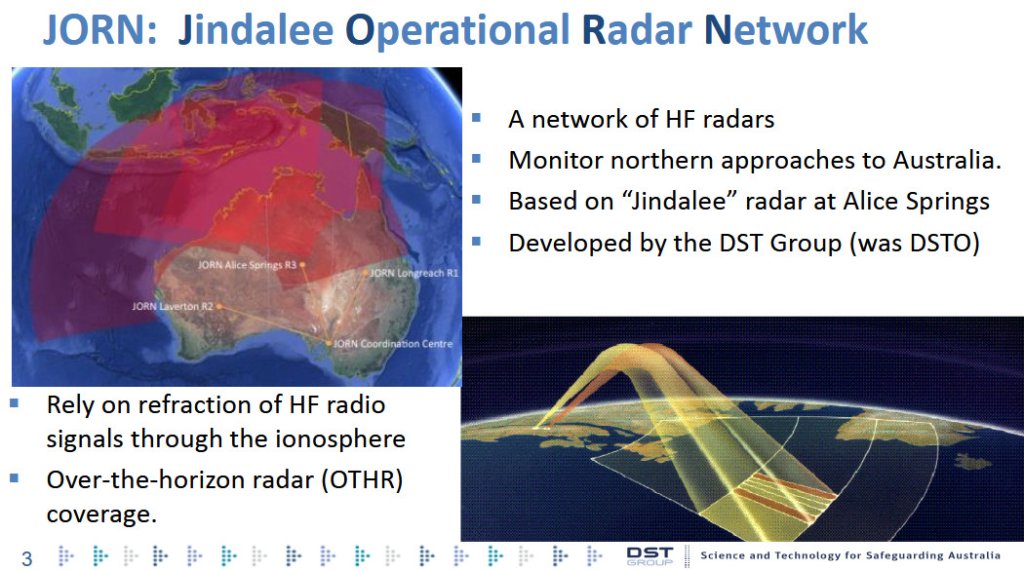
But that fence line was put in place when bombers had to cross it to shoot something, because of the range of their weapons. It’s still relevant in that you will find a weapon crossing that, but bombers don’t need to cross that line. So the fundamental issue is they could be in international airspace, well north of us, and conduct a launch. And so that’s my challenge – how do I domain sense? How am I aware of what’s going on, from a domain awareness point of view, to know that they are there? I think we have to up our game. So Canada’s invested recently in the Over the Horizon Radar project, where we’ve bought the Australian system known as JORN [Jindalee Operational Radar Network].
(We’ll discuss the Over the Horizon Radar project in more detail later in this interview)
Q: Have you seen any combined threats from China and Russia since that bomber flight?
A: They continue to conduct combined bomber patrols, but most typically, in the Indo-Pacific, in and around Japan and around the Korean Peninsula. We have not yet seen another return of a combined bomber patrol into the North American approaches.
Q: Are you seeing any recent joint Chinese-Russian naval patrols?
A: China routinely has these auxiliary general intelligence vessels, which are dual-use vessels, that transit the Bering Sea and end up in what I would characterize as the 10 o’clock to North America, if you look at North America like a clock. So that certainly is an activity that is concerning. Russian research vessels are up there as well. And I think they’re up to some interesting things, and we are present to meet them when they are in the approaches to North America. So I had aircraft deployed up into Alaska this summer, and we were on 14- or 15-hour missions up to 88 Degrees north to make sure we were over top of these vessels as they approached the continent.

Q: You said these vessels are up to some interesting things. What interesting things?
A: Well, I think they, they’re obviously mapping, they’re mapping the seabed for a variety of purposes, both scientific and military. And I think I just leave it at that.
Q: Do you know if they’re looking at underwater cables and that kind of infrastructure?
A: I think yes to all that. I’m not going to get into it in an unclassified setting, but I would just say I’m very concerned about some of the increased activity in that region, and certainly a region that is pristine. It’s also very difficult to navigate through from an underwater point of view. And so there’s a reason they would be up there. I don’t know quite what it is, but it’s concerning from a North American point of view.

Q: Russia has traditionally been the primary threat in the far north, but China’s military expansion in the Arctic is changing this. What role do you see China playing in the Arctic in the coming years?
A: The Russia-China piece is a bit of a marriage of convenience. And we’ll see where this goes. It could deepen, but I certainly don’t see it as close a binational command as we have with the U.S. and Canada, where we have NORAD aircraft flying in tight formation with each other, relieving each other on station, protecting our two countries seamlessly across the border. I flow my fighters into the U.S. and U.S. fighters flow into Canada as required. I don’t believe the Russia-China relationship is that way. I think it’s deconflicted in time and space. They present, obviously, a challenge to North America with these combined power patrols, but I don’t see it anywhere as deep as the relationship we have.

Q: But beyond a relationship with Russia, how do you see China on its own playing a role in the Arctic in the coming years?
A: They have a lot of ambitions, and they’re building a lot of military capability, which we need to pay attention to, in the air domain and the maritime domain, specifically in space, the cyber domain. So I worry quite a bit about the expansion beyond the First and Second island chains of their sphere of influence, and what they wish to do. And I think economic security is national security and vice versa. So you can’t disentangle one from the other, and that’s the advice we give our government.
Q: Can you offer more details about how you view the threats from China?
A: They have fifth-generation aircraft and sixth-generation aircraft and sixth-generation aircraft in development. They have long-range air-to-air weapons, which I get concerned about. Obviously, they have aircraft carrier capability, a Rocket Forces capability, which can reach out and touch into our allies’ homelands. You have a pretty significant subsurface capability that’s growing by the day with the Shang class submarine.

So I think there are threats that emanate in almost every domain. I don’t worry too much about the land domain, but I do worry about long-range threats that emanate from the land domain, that is to say, Rocket Forces. So maybe just leave it at that. I don’t want to get into an intelligence discussion because it’s probably not the right forum.
Q: Can you provide any new details about the still unidentified objects that flew over the U.S. in early 2023, including one that was shot down in Canadian airspace? Who sent them? Why hasn’t imagery and additional information been released about those objects?
A: I’m tracking one object that was shot down near White Horse using an F-22 under the NORAD agreement, obviously authorized by the Canadian government. I don’t believe they have found the wreckage of that thing yet. It’s a white balloon in the middle of a white expanse of snow, so it is actually hard to find. We had Canadian military folks searching for it for weeks. As far as I know, we did not recover it. It was a balloon, either research or a state actor. It’s not known which. I can’t really give you that detail.

Q: You said you can’t give me that detail. Is it because you don’t know or can’t tell me?
A: I legitimately don’t know (laughs). I will say the way that we executed the engagement, though, is exactly how NORAD’s agreement was crafted to work in the sense that sovereign decision, sovereign soil, but by national best sensor, best shooter. So it actually worked out exactly as scripted.
Q: There were other objects spotted in the skies around the same general time period that we still don’t know what they were or there hasn’t been any additional imagery or information released. Can you talk about those situations?
A: We do track a fair number of research balloons that move around the planet, and you need to sort of run some algorithms on your radar takes to find them. Sometimes it’s very small, like, just imagine, it’s not emitting any heat. It’s got almost no radar reflectivity. These are very hard to detect items. But I don’t have any other information to provide on balloons or UFOs or otherwise.

Q: Let’s circle back to the Arctic Over the Horizon radar. Are there any updates you can provide? What will it bring to the table that doesn’t exist today? And can you talk about the cost overruns associated with the program?
A: I wouldn’t say cost overruns. I just think the understanding of what the system is and what it can do is sort of evolving. So we bought some land in southern Ontario for a transmit site and receive sites. You might be aware that Over the Horizon radar is a bit of dark magic, in the sense that you need about 80 miles between a transmit and receive site.
The receive sites are these three-kilometer by five-kilometer boxes of many thousands of antennas, in some cases, 30,000 antennas. And you can progressively build out that array to have a higher fidelity in your radar in terms of the rare cross-section size that you can see. The transmit site will be full power when we build that for 2029. The receive sites we will build out over the years, as we get more and more space to build on.
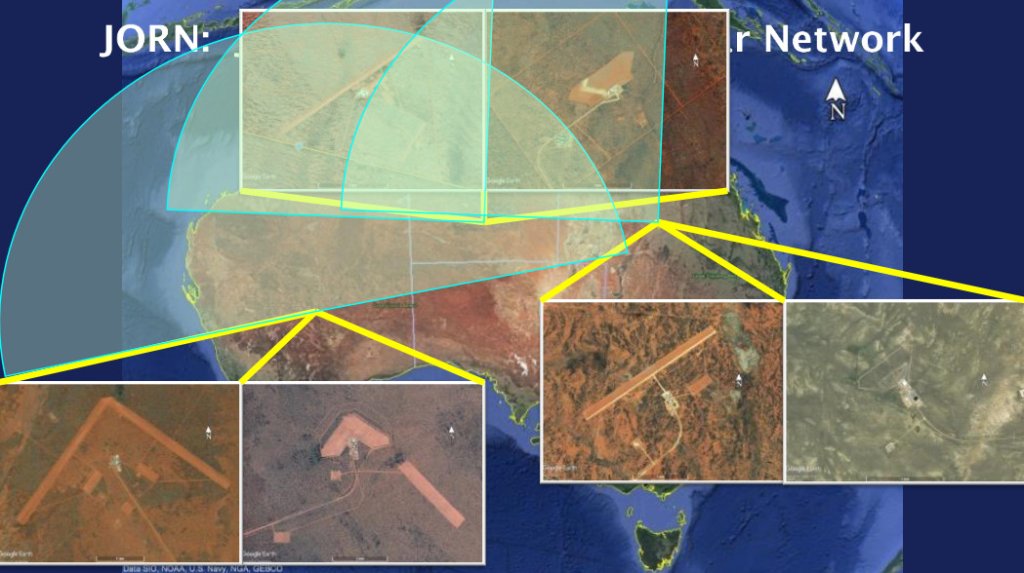
If you look at the radar picture in the United States, there are so many airports through the center of the U.S. that you never really leave radar coverage, at least in the lower U.S. Canada is not the same. Most of our population is along our border with the U.S., and as you know, the center is quite empty. So you do have little pockets of folks living near an international airport. You get a radar associated with that. And then you have the North Warning System, which is up at around 72ish [degrees] north. So there are large swaths that are sort of unsurveilled, unless you were to put an AWACS aircraft there to go look at it.

What this will do is give us the ability to sense. Over the Horizon radar is different, though. It’s not like this sort of sweep that you would get with a normal radar. You have to plan it like you’re looking at trapezoids, a couple of hundred miles by a couple of hundred miles that you soak with radar energy. You’re bouncing energy off the ionosphere, into that trapezoid, and then there’s a revisit rate. Every so many seconds, you’re re-irradiating that trapezoid. And that gives you your change detection of a track moving.
Certainly, I’ve seen the Australian system at work. They have three radars in the middle of Australia that look north towards China, towards the Indo Pacific, and their remote sensing unit down in Adelaide, aggregates those signals, and they present a recognized air picture using that, and it’s pretty, pretty dramatically good. I’ve seen high-end aircraft moving through the South China Sea.
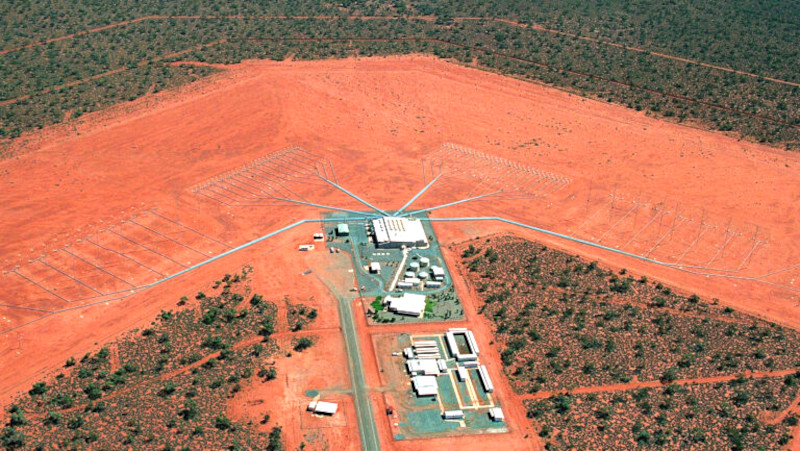

Australia has been operating a version of that for decades now. They’re, quite honestly, world experts on HF over-the-horizon radar. And we’re replacing a couple of sites in the south of Canada. The first few sites are going to look towards the Greenland, Iceland, UK (GIUK) gap.
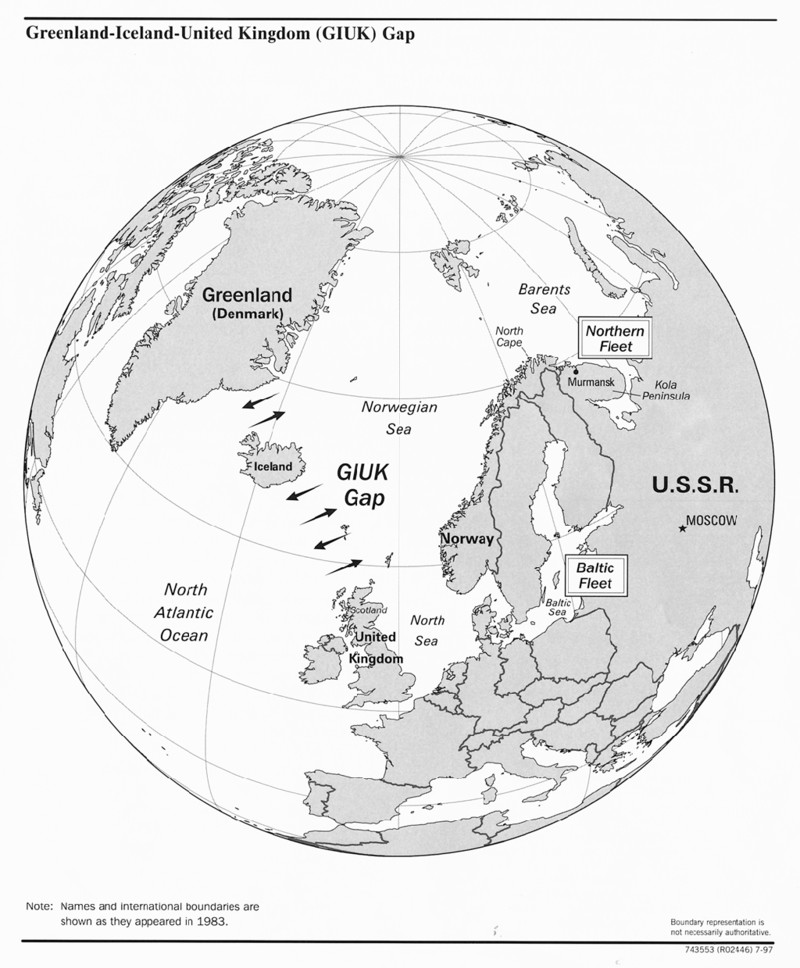
And the second set of sites is going to look to the northwest. And those are going in by 2029 to 2031. We bought the land. We’re clearing the land now. We’ve got a partnership with Australia. So using HF energy to be able to see into the Arctic is useful. And I think space-based sensors, space-based AMTI [air moving-target indicators], space-based intelligence. These are the things we’re going to be using, I think, to look and sense in the Arctic.
Q: What’s the range of the Over the Horizon radar?
A: I believe it’s 3,000ish kilometers, unclassified. But it all depends. You have to have ionospheric sounders that bounce and give you the texture of the ionosphere. So you can tune your radar to bounce it. So again. It’s a bit of a dark art. It depends on the ionosphere conditions of the day. So you want to pair it, obviously, with space-based [sensors] to make sure you have a layered domain awareness approach.
Q: And what does Over the Horizon radar bring to the table that doesn’t exist today in terms of seeing what’s out there?
A: It’s the ability to have a much cleaner and more complete picture of any target that is moving in the air or on the water, and our challenge is maritime domain awareness. Maritime warning is part of the NORAD mission set, so being able to sense on the surface of the ocean at great distances is really important. The challenge with Over the Horizon radar, for the Canadian Arctic context, is a thing called the auroral oval, where all of that energy sits. That gives us those awesome northern lights in Canada. It also prevents HF energy from bouncing into that oval. And so you do need something inside a transmit and receive site, inside of the pole.

And so we have a signals intelligence base way up north on alert called CFS [Canada Forces Station] Alert, named for a British ship that was stranded there in the 1800s. It’s the most northern permanently inhabited place on the planet. We’ve got about 60ish, very, very dedicated RCAF and Canadian Armed Forces people who live up there on six-month shifts. And that is a great place to put a transmit site. And there are receiver sites potential all over the place. In the Arctic, we have research stations that we’re looking at that have power and that have potentially fiber, depending on where you put it, that would allow you to get that data back south. But we need to transmit and receive in the north.

Q: Can you tell us about the development of the Crossbow sensor system and what that includes?
A: It’s a passive sensor. And so I won’t get into what it can do. I will say, in the Canadian Arctic, the challenge, obviously, is power generation and making sure that can be powered. And that’s what we’re focusing on. It’s the shelter that makes sure that we can feed that sensor.
Q: Where is Crossbow in the development phase?
A: We have some installations that have occurred in the last year or two. I’ll leave it at that.
In the final installment of our interview, McKenna talks about Golden Dome, space-based sensors and the dire need for airborne early warning and control aircraft.
Contact the author: howard@thewarzone.com
