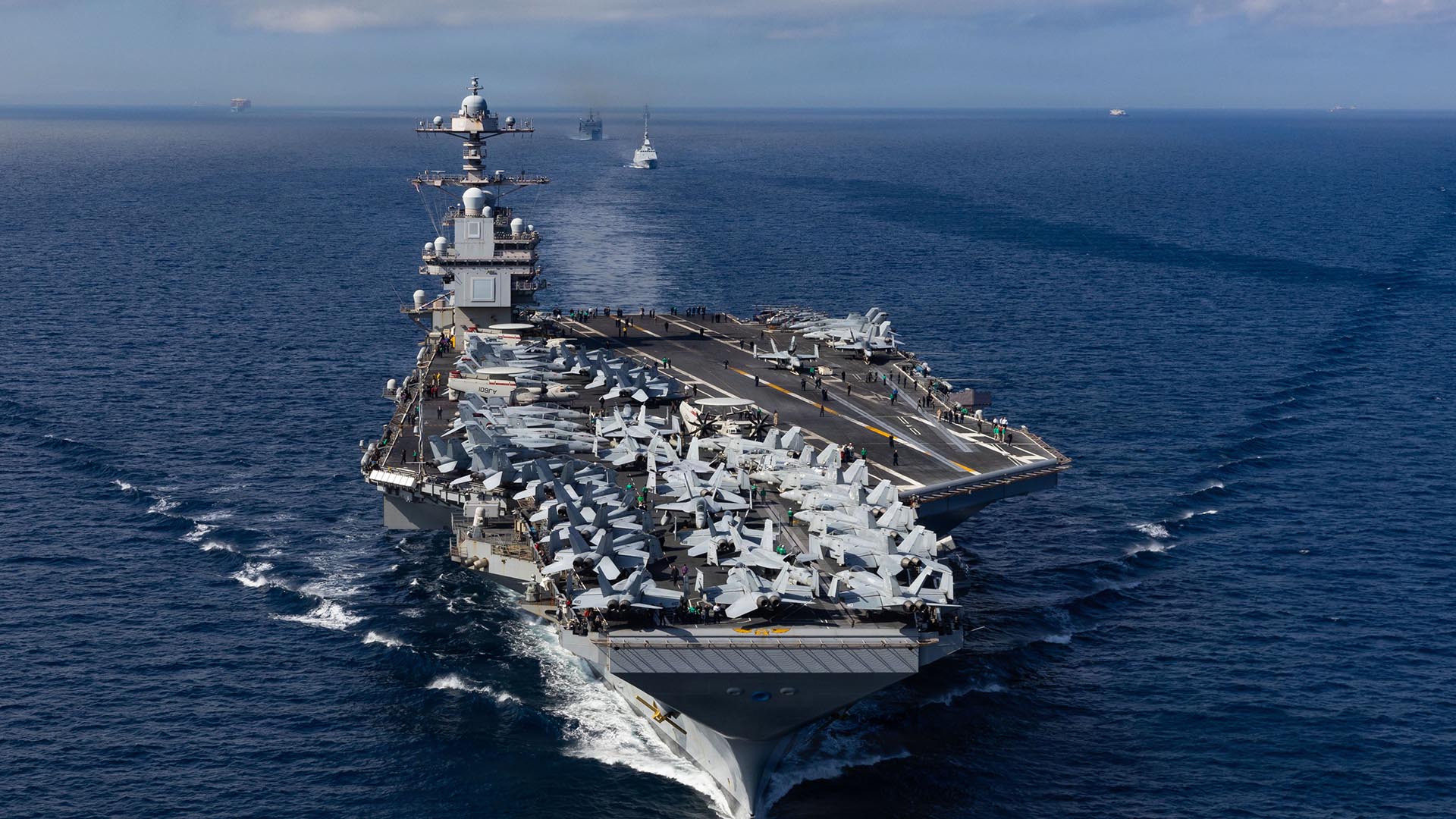
The decision to send the Ford Carrier Strike Group (CSG) from the Caribbean to the Middle East was made after the Navy’s top officer said he would give “push back” against such an order over concerns about the welfare of the crew and the condition of the ship after being deployed for so long. The carrier departed Norfolk last June for the Mediterranean. It was later dispatched to the Caribbean last October by President Donald Trump to take part in a mission that ultimately resulted in the capture of Venezuelan dictator Nicolas Maduro. Trump’s new deployment order for the Ford came as he is considering whether to attack Iran amid ongoing negotiations and after sending the Abraham Lincoln CSG to U.S. Central Command area of operations.
“I think the Ford, from its capability perspective, would be an invaluable option for any military thing the president wants to do,” Adm. Daryl Caudle, the Chief of Naval Operations (CNO), told a small group of reporters, including from The War Zone, last month at the Surface Navy Association’s (SNA) annual symposium. “But if it requires an extension, it’s going to get some push back from the CNO. And I will see if there is something else I can do.”
Caudle didn’t provide any specifics about what actions he would take to forestall an extension.

Regardless, the order to send the Ford CSG to the Middle East will extend its time away from its homeport even further. The ship won’t even get to the region until near the end of this month and it’s unclear how long it will be needed there, although Trump has mentioned something of a loose timeline.
“I guess over the next month, something like that,” Trump said Thursday in response to a question about his timeline for striking a deal with Iran on its nuclear program. “It should happen quickly. They should agree very quickly.”
There is also a chance that the Ford could be ordered to turn around should a deal be reached with Iran.
Trump also said it would be “very traumatic” for Iran should no deal be reached.
On Friday, Trump gave reporters his rationale for ordering the Ford to the Middle East.
“We’ll need it if we don’t make a deal,” the U.S. president told reporters.
“The strike group’s current deployment has already been extended once, and its sailors were expecting to come home in early March,” The New York Times, which was first to report that the Ford was ordered to the Middle East, noted. “The new delay will further jeopardize the Ford’s scheduled dry dock period in Virginia, where major upgrades and repairs have been planned.”
It is publicly unknown what discussions the CNO had with senior administration and Pentagon officials and whether he raised any objections or sought alternatives to keeping the Ford at sea longer than anticipated. We have reached out to his office and will update this story with any details provided. We also reached out to the White House and Joint Chiefs of Staff, which referred us to the CNO’s office.
At the SNA conference, Caudle emphasized that there is a price to be paid for the strike group after being away from homeport for more than 200 days under often intense conditions. That was almost exactly a month ago.

“I am a big non-fan of extensions, and because they do have significant impact,” Caudle explained. “Number one, I’m a sailors-first CNO. People want to have some type of certainty that they’re going to do a seven-month deployment.”
Beyond affecting people, extensions also have a detrimental impact on the ship in addition to its previously noted dry dock schedule.
“So now, when the ship comes back, we expected the ship to be in this level of state in which it was used during that seven-month deployment, when it goes eight, nine-plus months, those critical components that we weren’t expecting to repair are now on the table,” Caudle pointed out. “The work package grows, so that’s disruptive.”
In addition to the maintenance issues Caudle brought up at the SNA conference, the Ford also is also plagued by sewage issues.
You can read more about how detrimental deferred maintenance is to carriers — or any U.S. Navy warship for that matter — that get their deployments extended in our deep dive here.
It is not unusual for there to be two carriers deployed to the Middle East region. For instance, a year ago, the U.S. Navy had both the USS Harry S. Truman and the USS Carl Vinson aircraft carriers in the Middle East at the same time, engaged in combat operations against Yemen-based Houthi rebels. However, the Navy has 10 active carriers after the Nimitz, the service’s oldest, returned to port in December ahead of a scheduled decommissioning. There are scheduling and logistical support limits to how many can be out at sea at the same time without massive disruptions down the line.
The USS Eisenhower, the last carrier to make an extended deployment, has seen its planned maintenance extended for a half year and counting as a result of the additional strain of being away from its home port for so long. The Navy’s Fiscal Year 2026 budget shows that work on the ship was supposed to have been completed last July, but it is still unfinished. The lack of availability reverberates across the rest of the fleet. That in turn limits the options commanders have when planning or preparing for contingencies and puts the overall carrier availability plan out of whack.
As for the rest of the fleet, three other carriers are in various maintenance periods taking them out of action for extended periods. In addition, the USS George Washington is forward deployed to Japan, two carriers are preparing for deployment and two are in post-deployment mode.
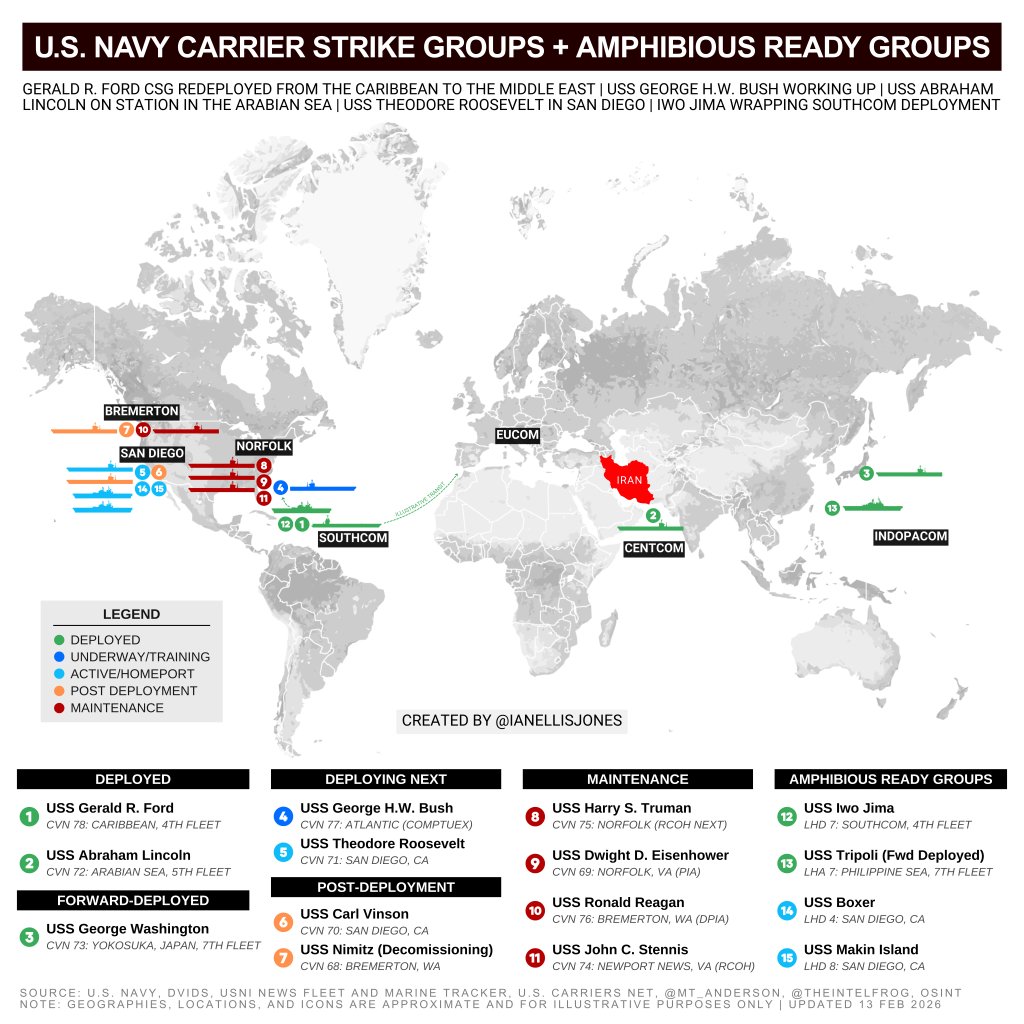
The move to send the Ford to the Middle East comes amid a growing buildup of forces ahead of a potential conflict with Iran. In addition to the Ford, the Pentagon is also dispatching a peculiarly small number of Air Force tactical aircraft to the Middle East, joining a limited number of aircraft already there on land and sea.
In addition to the Lincoln, there are also at least nine other warships in the region, including five Arleigh Burke class guided missile destroyers. Submarines are also there, but their presence is not disclosed, and there are more than 30,000 troops on bases around the Middle East.
Another CSG, with its embarked tactical aircraft and Aegis-equipped escorts, would certainly bolster America’s firepower in the Middle East. As we have frequently pointed out, even with the jets that are there and those arriving, there is not enough tactical airpower there now for a major sustained operation. A second CSG would provide significant help.
It remains unknown what orders Trump will give or when, but a second carrier strike group in the region gives him more options.
Contact the author: howard@thewarzone.com
