Ukraine’s President Volodymyr Zelensky has announced that his country has begun using homegrown Sapsan (which means peregrine falcon) ballistic missiles in combat against Russia. While the claim may be disinformation, such a weapon would give Ukraine a highly valuable new standoff strike option, unlike any other in its inventory. It would also not be subject to any foreign restrictions on its use, as it continues to be the case with many longer-ranged weapons supplied by the United States and other Western partners.
“Ukraine is already using the Neptune, the long-range Neptune, the Palyanytsya, the Flamingo. And also, the Sapsan, I’ll be honest — we’ve begun using it,” Zelensky told journalists. The Ukrainian president added that he would not disclose how many of these weapons have been deployed, or what they targeted.
“Because for now we don’t want the enemy to know all the precedents and all the details,” Zelensky added.
As well as the Sapsan, Zelensky referred to four domestically produced weapons that we already knew had been used operationally. These are the land-attack version of the Neptune anti-ship cruise missile, the extended-range version of the same weapon, known as the Long Neptune, the Palyanytsya jet-powered missile/drone hybrid, and the very long-range Flamingo cruise missile.
It’s clear, too, that Zelensky wants to promote confusion among Russian authorities as to which of these weapons are being used in any given strike.
“There are many cases when our enemy believes a strike was carried out with a Neptune… And let them continue thinking that,” he added.
With that in mind, we should also consider the possibility that the Sapsan has not actually been used in combat. So far, there doesn’t seem to be any confirmed evidence of wreckage from impact sites in Russia, although the Russian Ministry of Defense has previously claimed that it successfully shot down examples of Ukrainian ballistic missiles over Crimea.
On the other hand, using the Sapsan in combat would certainly make sense, given Ukraine’s extensive efforts to ramp up domestic arms production, with a particular focus on the ability to hit targets deeper inside Russia.
As well as the aforementioned long-range missiles, Ukraine has also made use of an extensive array of domestically produced long-range kamikaze drones, as well as other munitions that blur the line between those weapons and traditional cruise missiles, like the Peklo ‘missile drone’.
As for Ukraine’s domestic ballistic missile program, the results remain much less clear, but we have been waiting to see a weapon of this kind deployed for a long time now. Perhaps, its development has also been accelerated by help from Western partners.
In August of 2024, Zelensky announced the first successful test of a new domestically developed ballistic missile, now understood to be the Sapsan.
While details of the Sapsan remain scarce, the missile is closely related to the Hrim-2 (also written Grim-2 and which translates as Thunder-2 in English).
In fact, the Hrim-2 was developed as an export version of the original Sapsan, which had been intended for Ukrainian use.
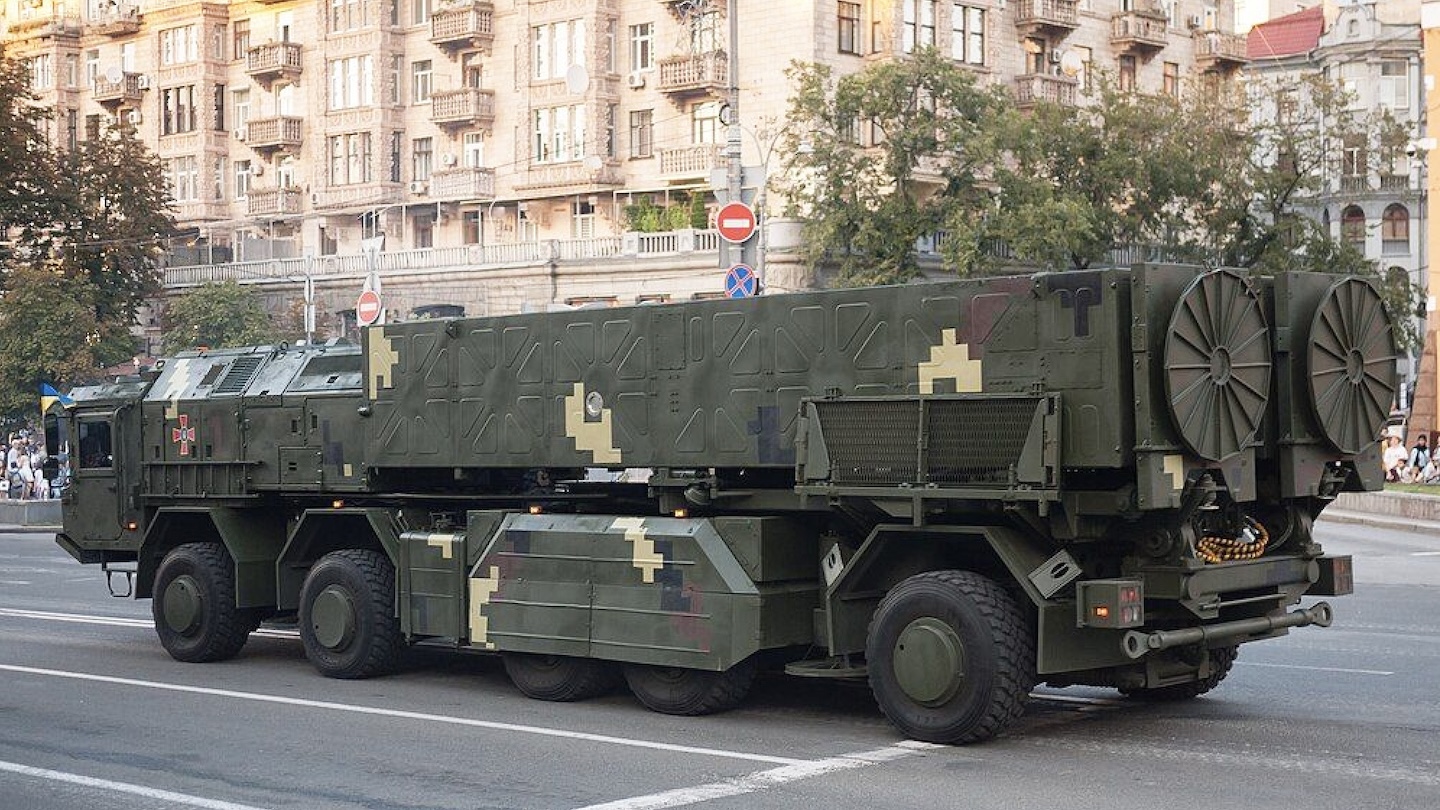
The origins of the Hrim-2 and its immediate predecessors date back to the late 2000s, with development apparently accelerated after Russia’s annexation of the Crimean peninsula in 2014. A rocket motor test associated with the design occurred in 2018, and the two-round, 10-wheeled transporter-erector-launcher (TEL) for the missile, or at least a mockup, appeared at a parade that same year.
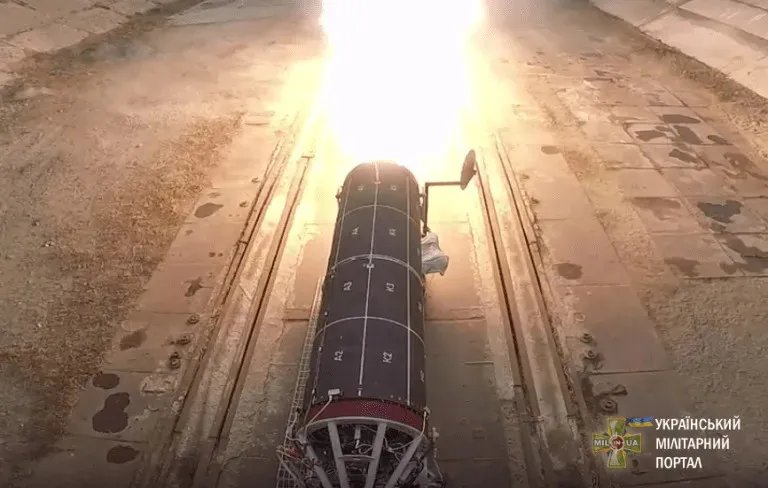

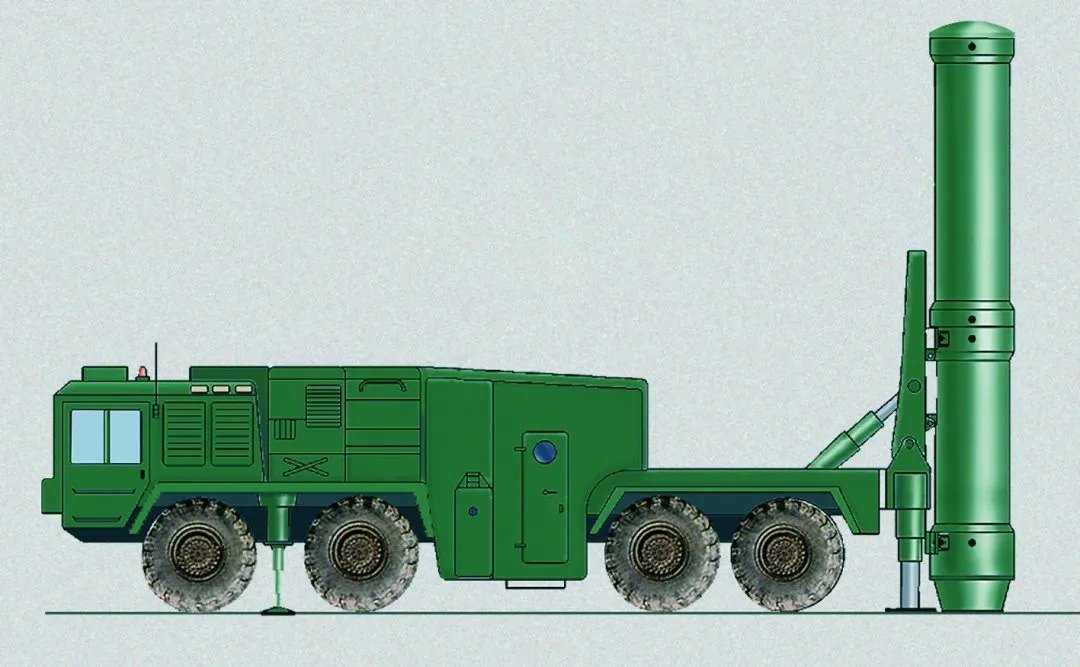
You can read more about what is known about the Hrim-2 and its development in this past War Zone piece, which followed speculation that Ukraine might have employed some of those missiles in an attack on Russia’s Saki Air Base in 2022.
While we don’t know what the Sapsan missile looks like, it is likely broadly similar to what we’ve seen of the Hrim-2 and preceding related designs, which, in turn, bear a superficial resemblance to Russia’s Iskander-M.
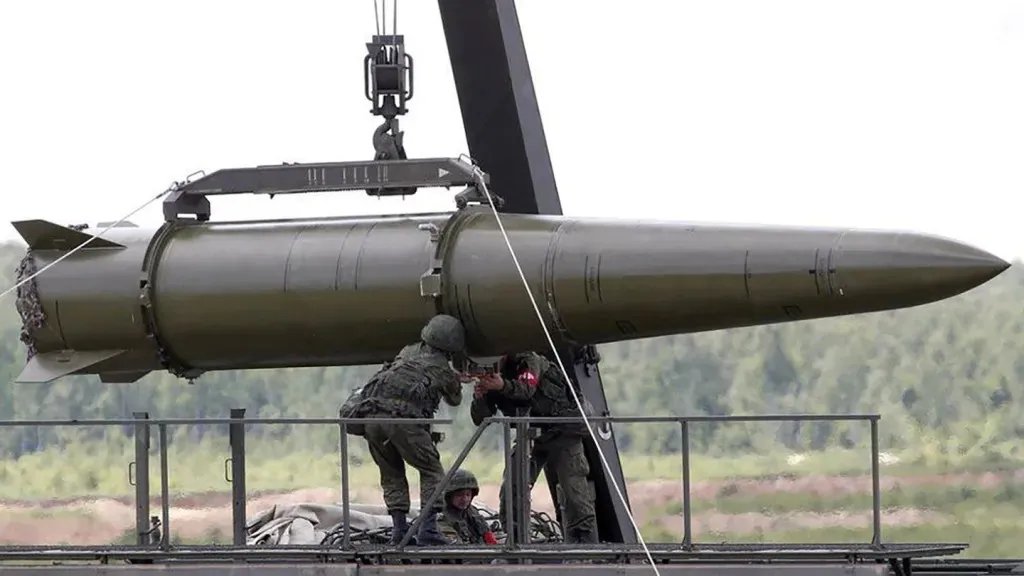


In terms of performance, the Hrim-2 reportedly has a range of at least 174 miles (280 kilometers) and possibly up to 310 miles (500 kilometers), and the same could well hold true for the Sapsan.
On the other hand, in 2023, Ukraine’s then-Minister of Defense Oleksii Reznikov also said that the country had a new long-range missile in development that could have a range of up to 620 miles (1,000 kilometers). This could also have been a direct reference to the Sapsan.
Regardless, it would seem highly likely that the Sapsan is in the category of short-range ballistic missiles (SRBM), which are traditionally defined as having maximum ranges of no more than 620 miles (1,000 kilometers).
Since the full-scale invasion, Ukraine has had only limited access to ballistic missiles, and none of these have come from domestic production.
The Ukrainian Armed Forces have been employing Soviet-era Tochka-U SRBMs, as well as even older Tochka types, both of which have the NATO reporting name SS-21 Scarab. These only have maximum ranges of 43 miles (70 kilometers) and 75 miles (120 kilometers), respectively, a fact that spurred the original development of the Sapsan/Hrim-2.

Furthermore, Ukraine has been receiving small numbers of ATACMS from the United States, which it has used to good effect.
However, in common with additional types of ground and air-launched standoff munitions supplied to Ukraine by the U.S. government and other foreign partners, there are strict limitations imposed on the use of those weapons on targets deeper inside Russia.
Putting all this together, the utility of a ballistic missile of domestic production becomes very clear, as part of a multi-pronged effort to strike key targets outside of Ukraine’s borders (as well as further beyond the front lines, in Russian-controlled territory).
As we have noted in the past, a new source of ballistic missiles that are more capable and longer ranged than the Tochka family, and that are not subject to any Western restrictions like ATACMS, would be a key breakthrough for Ukraine.
While long-range drones, cruise missiles, and drone/missile hybrids are valuable, ballistic missiles offer the advantage of very high speeds in the terminal phase of flight. This makes them much harder for enemy air and missile defenses to defeat. Ballistic missiles with unitary high-explosive warheads can also burrow down deeper into hardened targets or impart greater force on reinforced structures above ground, like bridges, thanks to that speed.
While we don’t know how Ukraine has employed Sapsan so far, provided that it has, a likely scenario would see the ballistic missiles combined with other types of missiles and drones in complex attacks to make it even harder for enemy forces to deal with. This would follow the same pattern that Russia routinely uses in large-scale attacks on Ukrainian targets.
If Ukraine is able to produce the Sapsan in meaningful numbers, and provided that it works to its full potential, the results could be significant, if it’s anything like the precedent set by Ukraine’s employment of American ATACMS.
Even with the restrictions imposed by the U.S. government, Ukrainian ATACMS strikes have led to major changes in Russian operating procedures, especially at airbases within range of those missiles. It has also forced Russia to move additional air and missile defenses to the theater, including the S-500, the most advanced surface-to-air missile system in the country’s inventory today.
At this point, we still need to await independent verification of the Sapsan ballistic missile being used in combat. However, the value of such a weapon for the Ukrainian military is unquestionable, providing a powerful new vector for launching standoff strikes into Russia without any foreign restrictions. Provided it is being used operationally, we likely won’t have to wait too much longer for positive confirmation of this.
Contact the author: thomas@thewarzone.com
