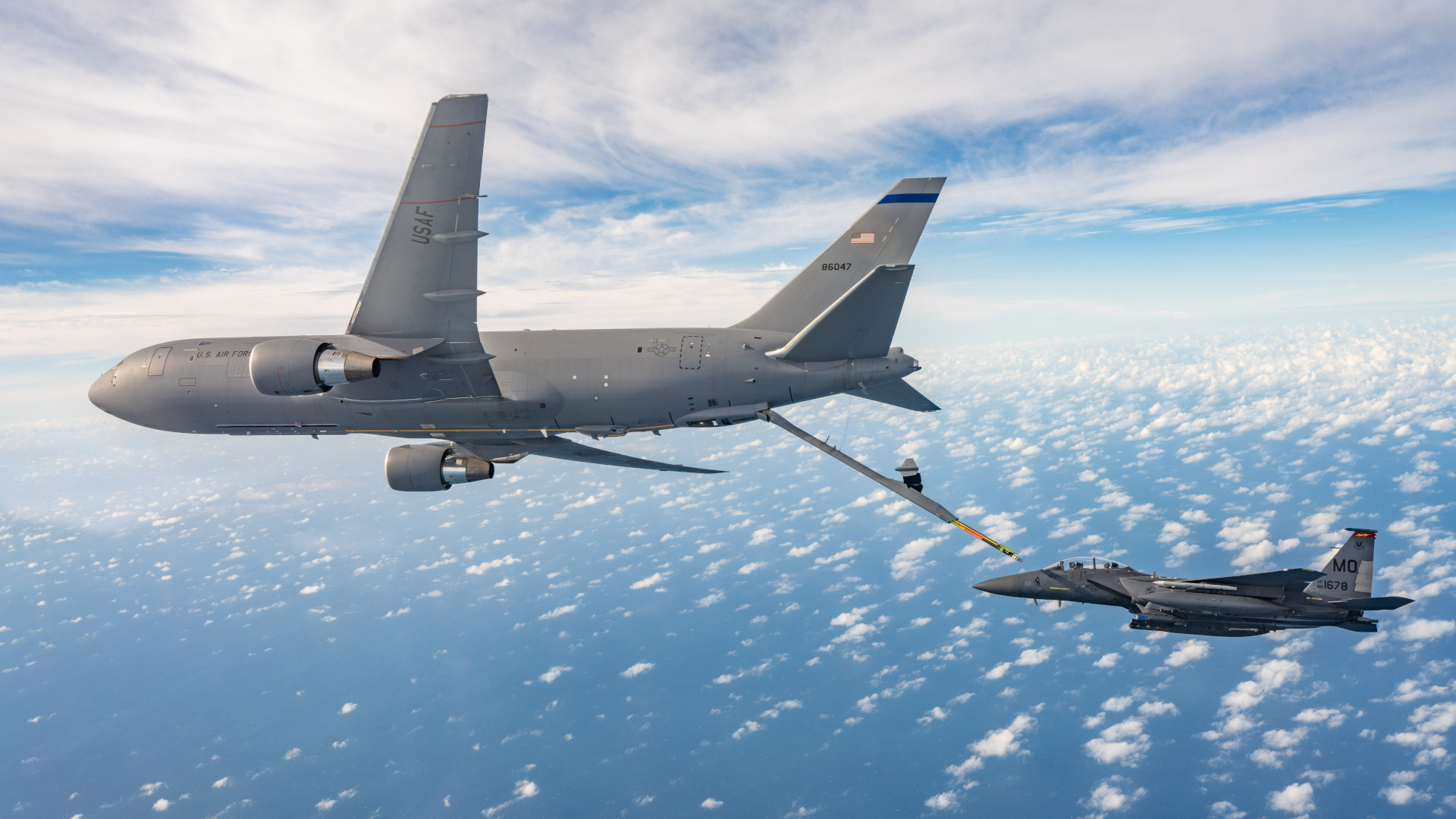
At least 20 U.S. Air Force tanker aircraft, 10 KC-46s and an equal number of KC-135s, supported the first day of the latest Bamboo Eagle exercise off the California coast, according to online flight tracking data. The first Bamboo Eagle occurred last year, as you can learn more about in this past TWZ feature. The large force exercise series has quickly become one of the most important for the U.S. military, as well as key allies, and has a clear eye on preparing for a future coalition fight in the Pacific with China.

The U.S. Air Force announced the start of Bamboo Eagle 25-1 yesterday. Like all previous iterations, the U.S. Air Force Warfare Center (USAFWC) at Nellis Air Force Base in Nevada has been leading the exercise, but units spread across many other bases, predominantly in California, are also participating. U.S. Air Force and U.S. Navy units are known to be taking part, but other branches have also been included in past iterations of Bamboo Eagle. Britain’s Royal Air Force (RAF) and the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) have also returned, and the Royal Canadian Air Force (RCAF) has joined the exercise for the first time.

As already noted, online flight tracking data showed a large force of KC-46 and KC-135 tankers supporting day one of Bamboo Eagle 25-1. At least one RAF Voyager, the British name for the Airbus A330 Multi-Role Transport Aircraft (MRTT), was also tracked in the area.
At least a dozen tankers have also been tracked now supporting the second day of Bamboo Eagle 25-1.
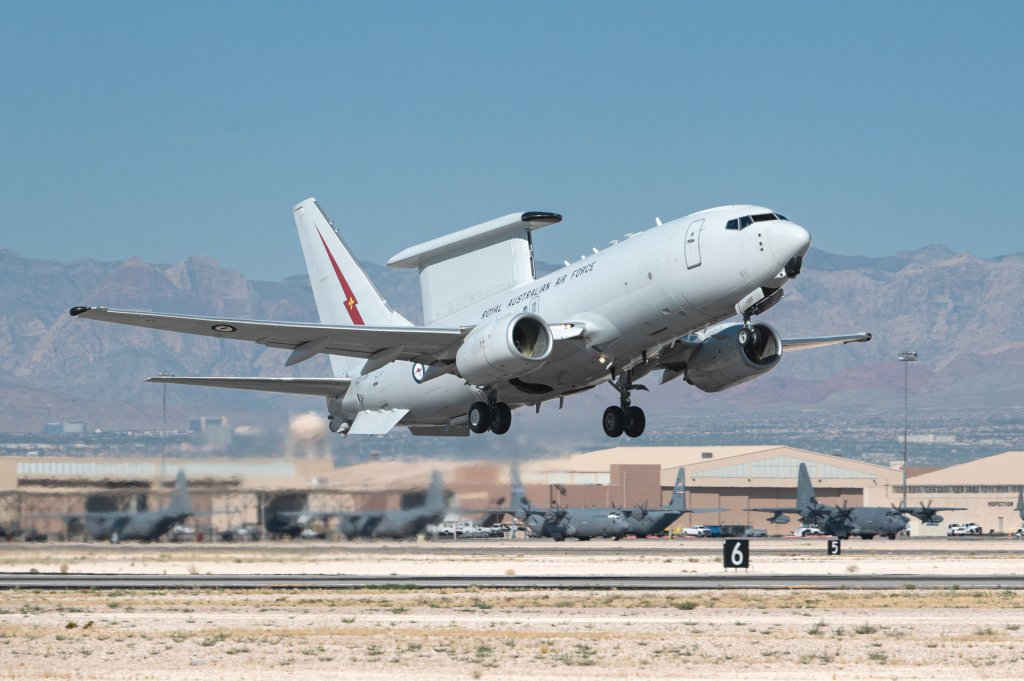
U.S. Air Force E-3 Sentry and RAAF E-7A Wedgetail airborne early warning and control aircraft were also present yesterday. It’s interesting to note here that the U.S. Air Force, the RAF, and NATO are in the process of acquiring Wedgetails to succeed their Sentry fleets.

An Air Force RC-135V/W Rivet Joint intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR) aircraft was also spotted likely supporting Bamboo Eagle 25-1 yesterday. However, Rivet Joints have been recently tracked flying over the Pacific off southern California, as well as elsewhere in the southwestern United States, as part of a surge of U.S. military support to border security operations opposite Mexico.
Not visible in the online flight tracking data from yesterday or today are the huge numbers of tactical jets that the tankers and other supporting aircraft were working with. In its announcement about the start of Bamboo Eagle 25-1, the Air Force included pictures of Air Force F-35A and RAF Typhoon FGR4 fighters, as well as Navy EA-18G Growler electronic warfare jets, taking part in Red Flag 25-1 at Nellis.
Red Flag is the U.S. Air Force’s premier air combat exercise series and recent iterations have been increasingly focused on operations in the Pacific. This in turn has put new emphasis on the range complexes off the coast of southern California, which offer larger areas in which to train on physically broader and otherwise more complex scenarios, and do so over water.
Red Flag is celebrating its 50th anniversary this year and the RAF and RAAF, among other key allies, are often participants. Other aircraft, including Air Force F-15E Strike Eagles and B-2 Spirit stealth bombers, as well as RAAF Growlers, took part in Red Flag 25-1, which flowed directly into Bamboo Eagle 25-1.
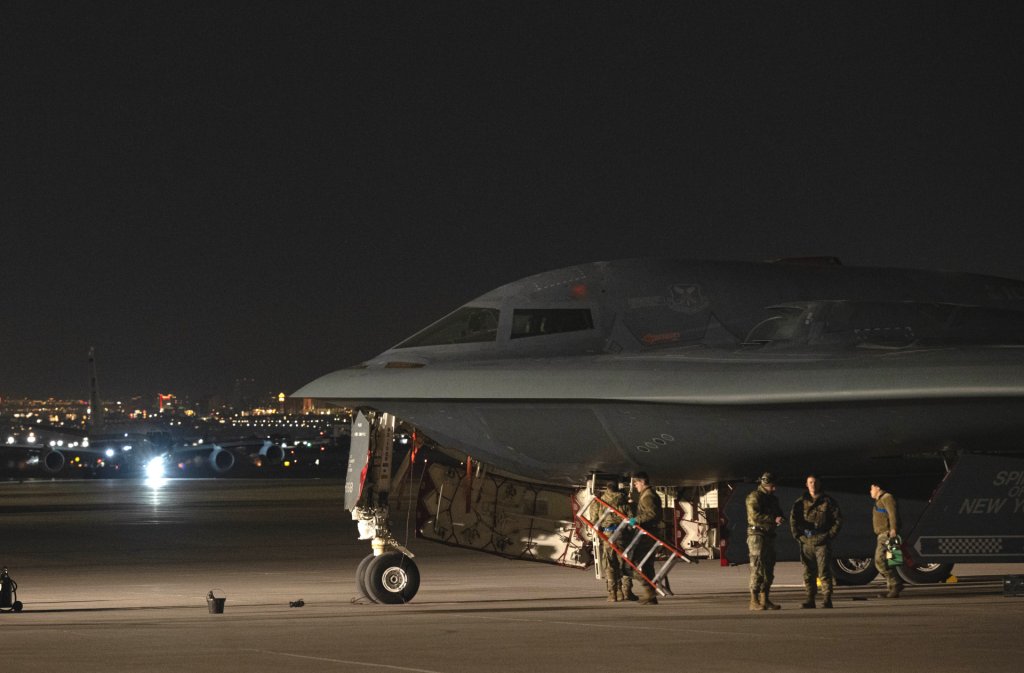
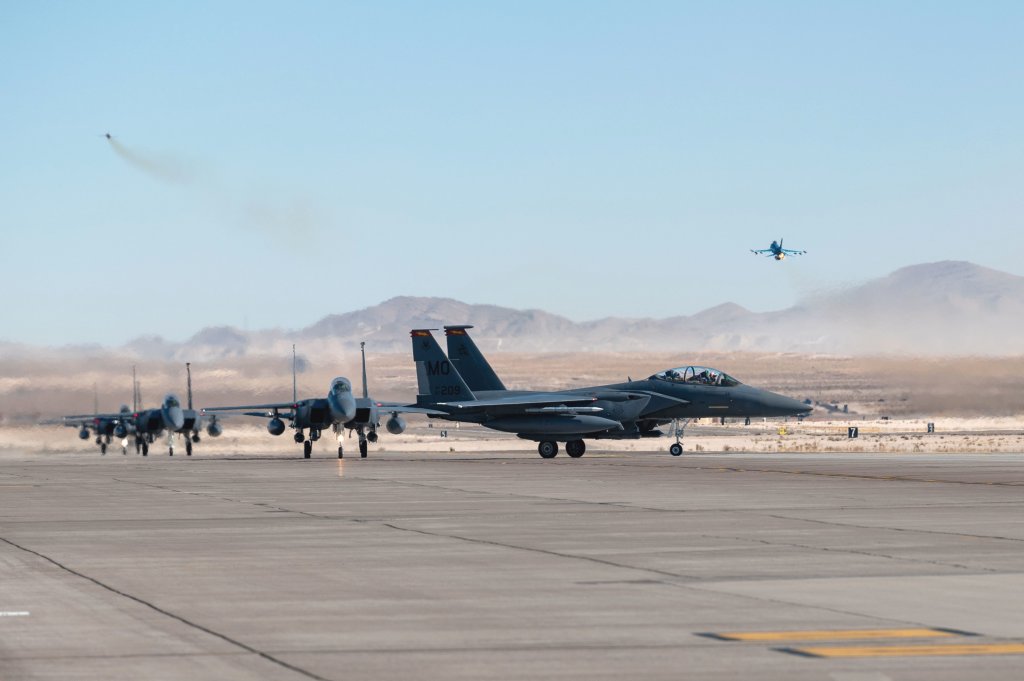
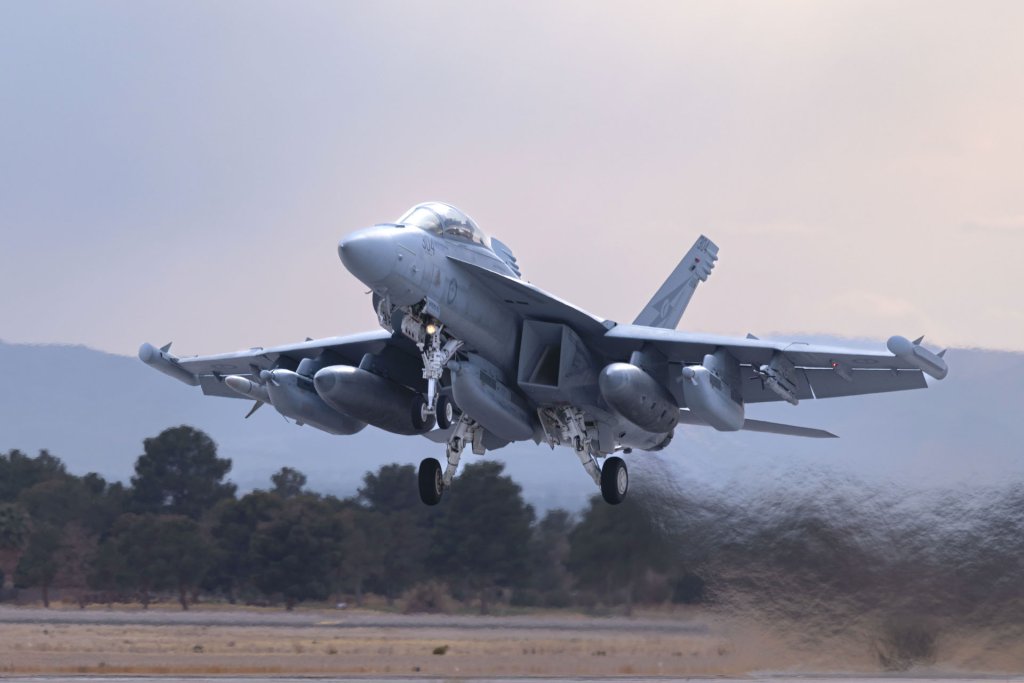




“This is the largest number of aircraft we’ve deployed for an exercise at Nellis (AFB) since we first attended Red Flag in 1980,” RAAF Group Capt. Stewart Seeney said in a statement yesterday. “These exercises provide a realistic training environment where we can integrate different capabilities and develop our ability to work with key allies and partners. For many of our aviators, deploying on these exercises is a career highlight and is not an experience that can be easily replicated elsewhere.”
F-35As from Hill Air Force Base in Utah are also notably operating from Naval Air Station North Island in California as part of the exercise. The Navy facility has been used as a staging point in past iterations of Bamboo Eagle. Air Force units using it for this purpose also have the opportunity to train around still-evolving rapid deployment and related concepts of operations, currently referred to collectively as Agile Combat Employment (ACE), which the service has been working on for years now. ACE has been and continues to be a central focus for Bamboo Eagle exercises, in general.
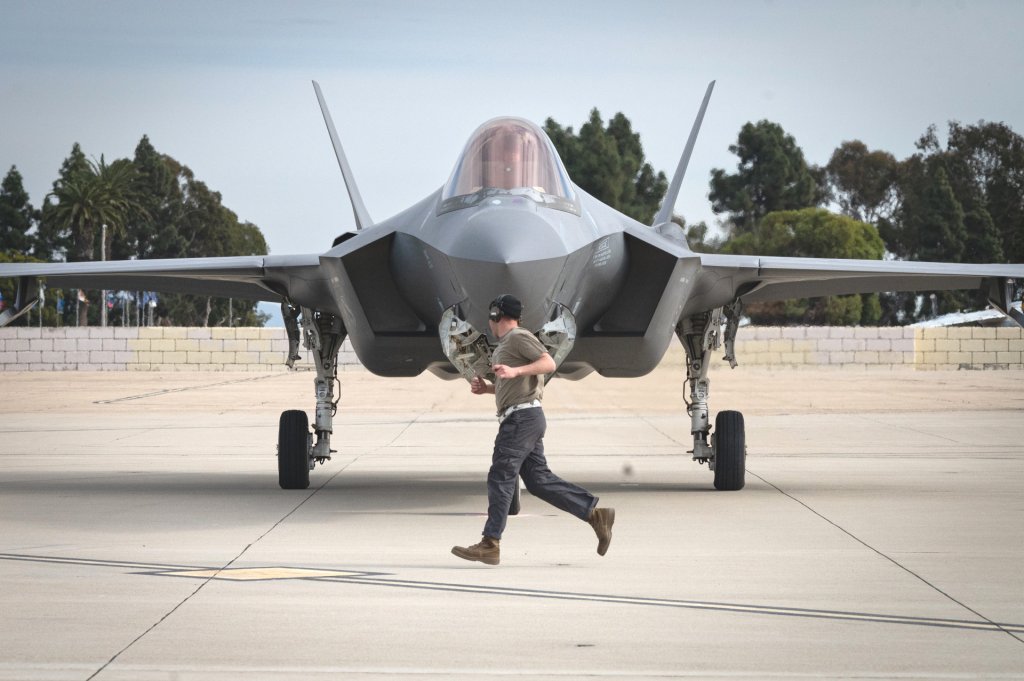

“We have had the luxury of operating from safe haven bases for many decades, and modern threats have fundamentally changed that reality,” Air Force Maj. Gen. Christopher Niemi, head of USAFWC also said in a statement. “Bamboo Eagle is a big part of helping us figure out how to manage those threats, and training together with our allies improves our ability to face those threats as a unified team.”
Other branches of the U.S. military, especially the U.S. Marine Corps, have been developing similar concepts of operations all centered heavily on ways to quickly deploy and redeploy forces throughout forward areas to upend enemy targeting cycles. Concerns about access to established bases, especially in the context of a potential future high-end fight in the Pacific, have been particular drivers of these efforts. There are growing calls for the U.S. military to do more to physically harden bases in the Pacific, along with other defensive improvements, which you can read more about here.

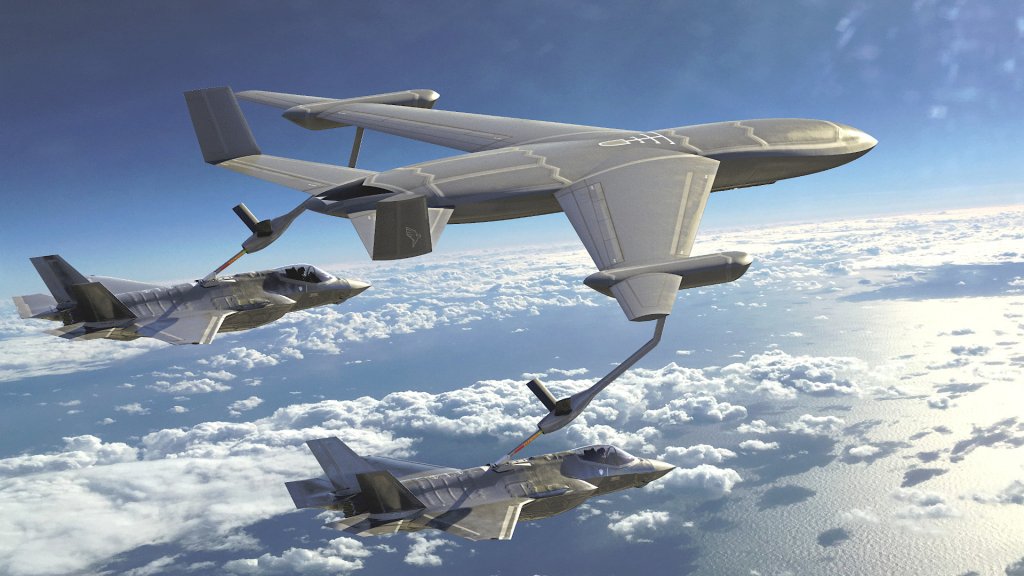
The prospect of a major conflict with China in the Pacific, where bases on the ground may be few and far between, has also been contributing to concerns about overall aerial refueling capacity, as well as the vulnerability of existing tankers. What has been seen from Bamboo Eagle 25-1 already underscores the critical importance of aerial refueling, especially for supporting shorter-legged tactical jets.
The Air Force is in the process of refining requirements for new stealth tankers and has also been exploring more novel options for increasing aerial refueling capacity. The Navy and Marine Corps, which have the added planning consideration of expeditionary aviation operations from carriers and other big deck ships, are also acutely aware of the issues at play. The Navy is planning to add MQ-25 Stingray drone tankers to its carrier air wings in the coming years and there is also interest in new options for extending the ranges of existing tactical jets. Private contractors, which can provide aerial refueling support for non-combat missions and help free up organic U.S. military tankers in the process, are another steadily growing part of the equation. There is significant uncertainty around future defense spending plans under President Donald Trump’s new administration, especially when it comes to Air Force modernization priorities like stealth tankers and other next-generation aircraft that were already facing affordability concerns.

Bamboo Eagle 25-1 also comes ahead of Air Force plans to stage a massive air combat exercise across the Pacific this summer, which you can read more about here. Dubbed REFORPAC, the exercise is expected to last some two weeks, days of which will be spent just getting forces to and from operating locations, underscoring the basic geographical challenges the region presents. At least some units taking part in REFORPAC are expected to go almost straight from that exercise into another iteration of Bamboo Eagle, as well.
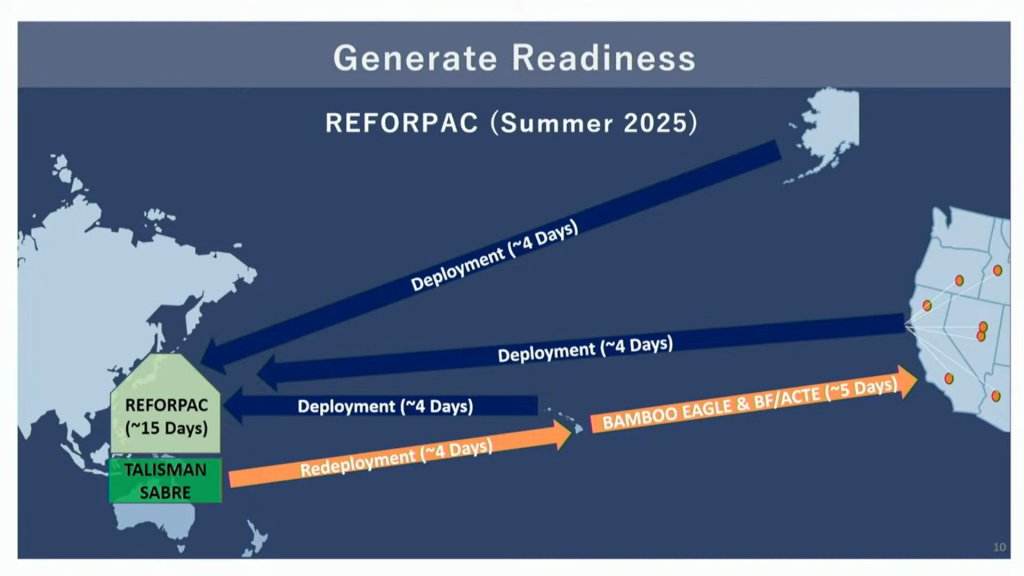
Bamboo Eagle exercises themselves only look set to continue expanding in scale and scope as important parts of broader preparations for a future major Pacific fight.
Contact the author: joe@twz.com
