The recent declassification of the United States’ Jumpseat spy satellite provides details on what was previously a highly secretive system, one that monitored critical Soviet military assets during some of the tensest years of the Cold War. While still redacted, the declassification provides never-before-seen imagery of a pioneering system that served the U.S. intelligence community for 35 years.

The declassification of certain elements of the Jumpseat program was announced by the director of the National Reconnaissance Office (NRO), the Pentagon intelligence branch responsible for U.S. government reconnaissance satellites.
There were eight satellite launches under Jumpseat (also known as AFP-711), between 1971 and 1987, one of them unsuccessful. Developed by the U.S. Air Force as part of the NRO’s Program A, the satellites were carried by Titan IIIB launch vehicles. Based on an original intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) design, these rockets lifted off from Vandenberg Air Force Base (now Vandenberg Space Force Base) in California.

The NRO confirms the mission numbers 7701 to 7708 for the eight Jumpseat launches. Analysts had previously attempted to match the Jumpseat missions to known space launches out of Vandenberg, although so far only the first and last of these have actually been declassified. There is a possibility that some of the launches normally assessed to involve Jumpseat actually carried other payloads.
As a signals-collection satellite, Jumpseat was an important part of the broader signals intelligence (SIGINT) community. In simple terms, SIGINT assets are used to detect and intercept communications and other electronic emissions. Whether radios or radars, those emitters can also be geolocated and categorized, as well as listened in on.
Jumpseat was also active in two subsets of SIGINT. The first was communications intelligence (COMINT), including keeping tabs on day-to-day communications between military personnel, by eavesdropping on electronic signals. Secondly, Jumpseat gathered foreign instrumentation signals intelligence (FISINT), which involves intercepting and analyzing electromagnetic emissions from foreign weapon systems, such as missile telemetry, radar, and tracking signals. Particular military emitters of interest to Jumpseat likely included air defenses and command and control nodes, with the data gathered being used to help build an electronic order of battle of an adversary nation, specifically the Soviet Union.

Jumpseat collections “were initially against other adversarial countries’ weapon systems capabilities,” the document states, without providing more details.
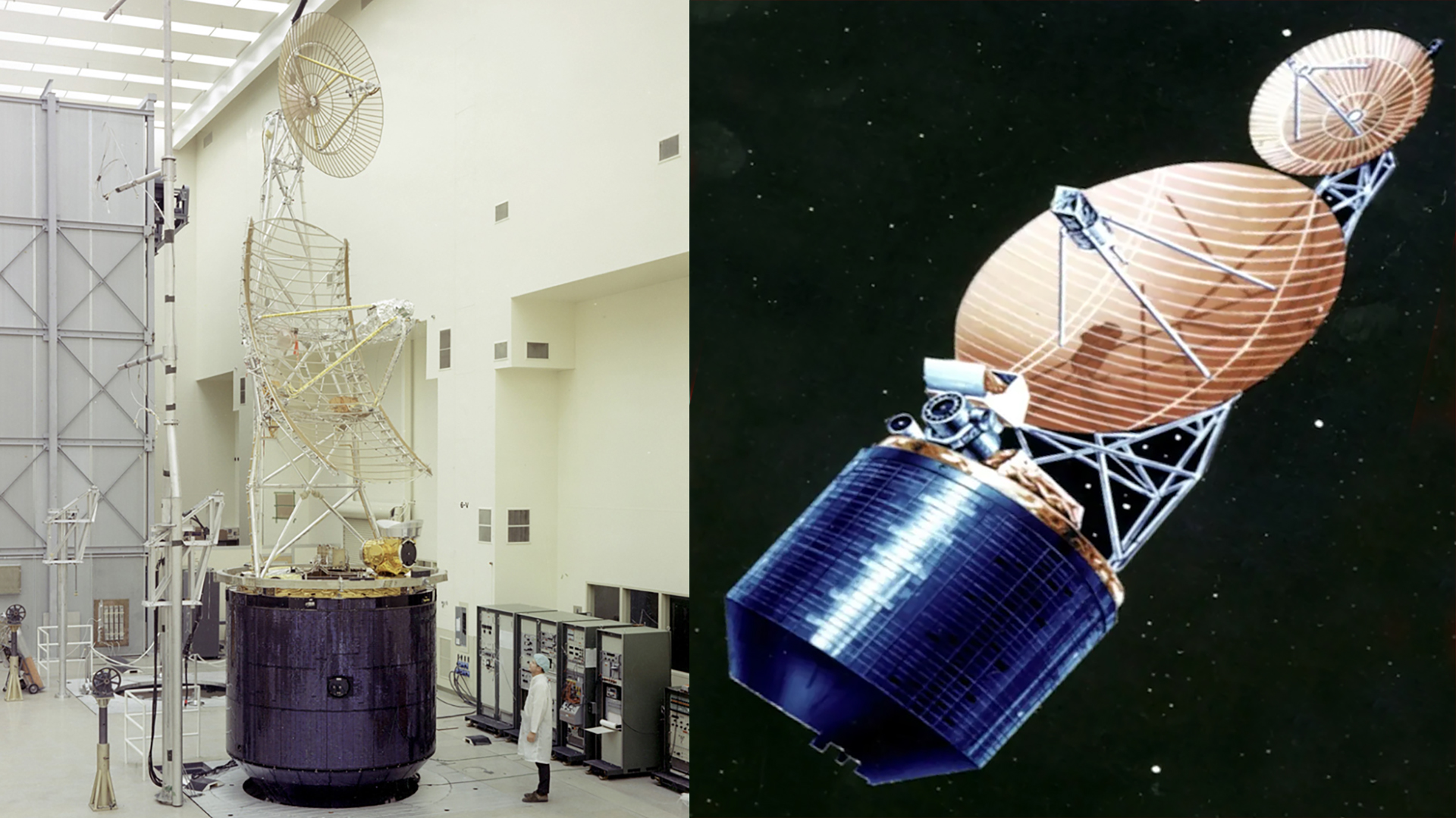
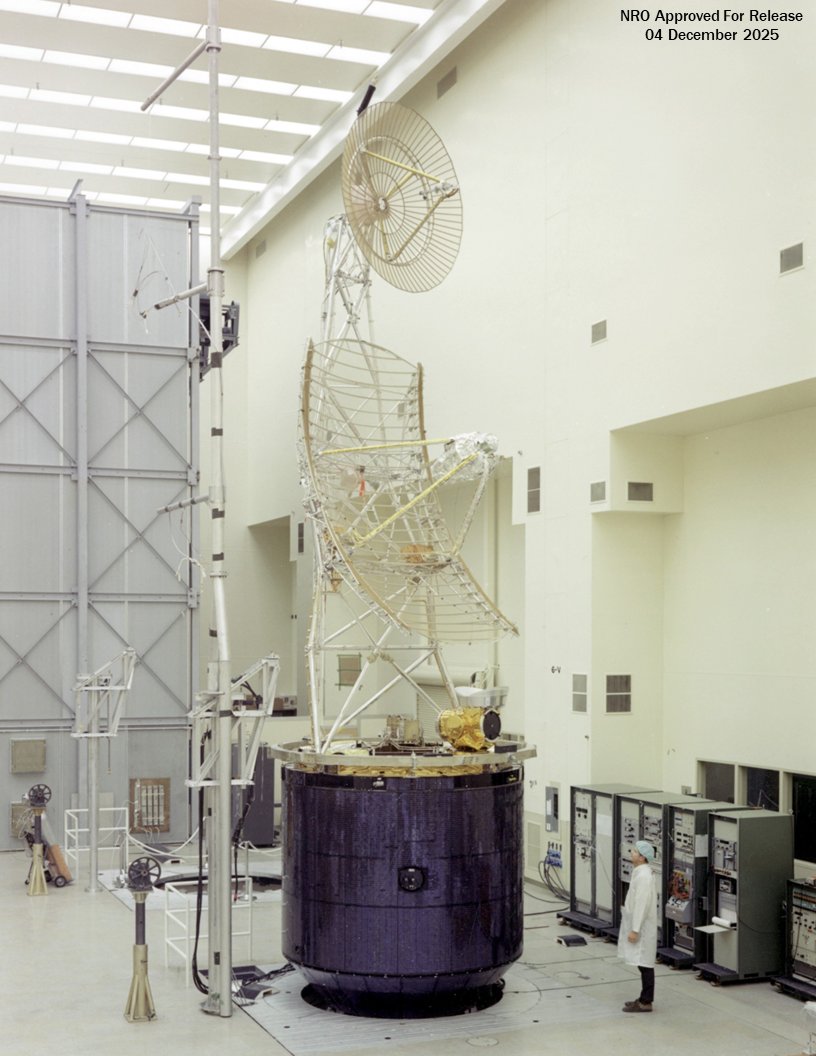
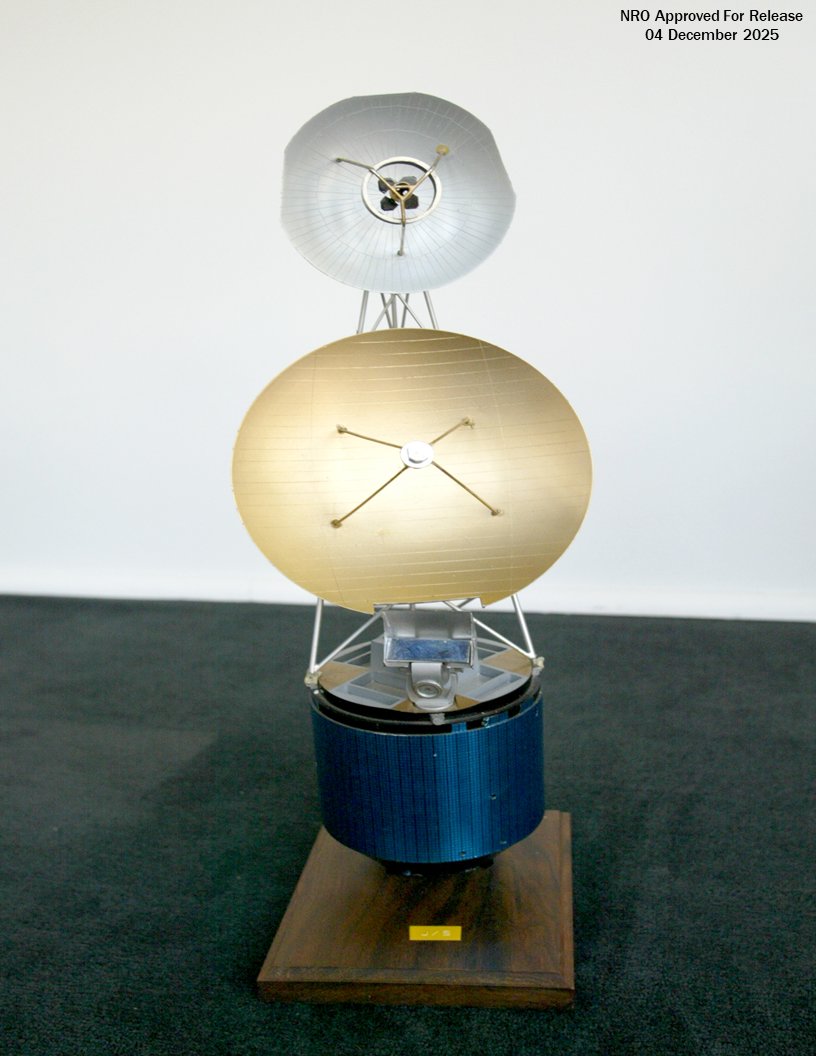
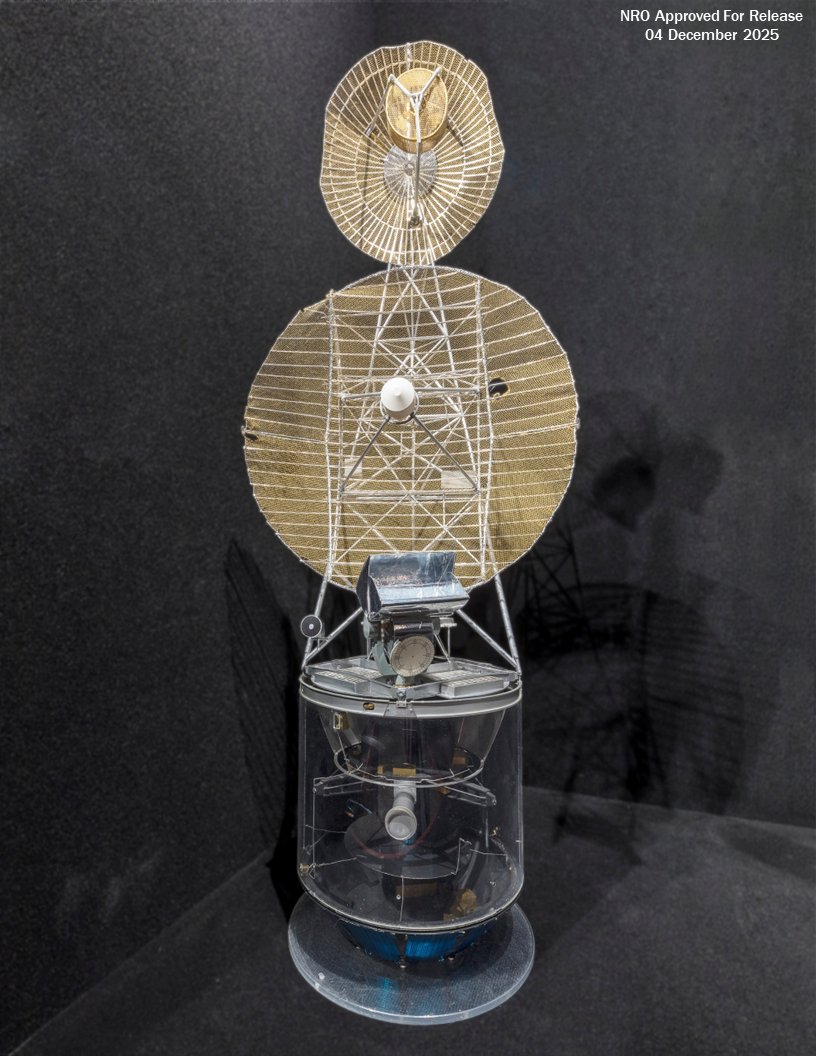
Previously classified imagery of Jumpseat has also been released, with the NRO providing a mix of diagrams, artwork, and photos of models and test specimens.
As far as is known, the Jumpseat satellites were built by Hughes, using a spin-stabilized bus, similar to that used in the TACSAT and the Intelsat-4 communications satellites. Key features of Jumpseat included a large, partially foldable dish antenna for data collection, as well as a smaller dish antenna to send data back to the ground.
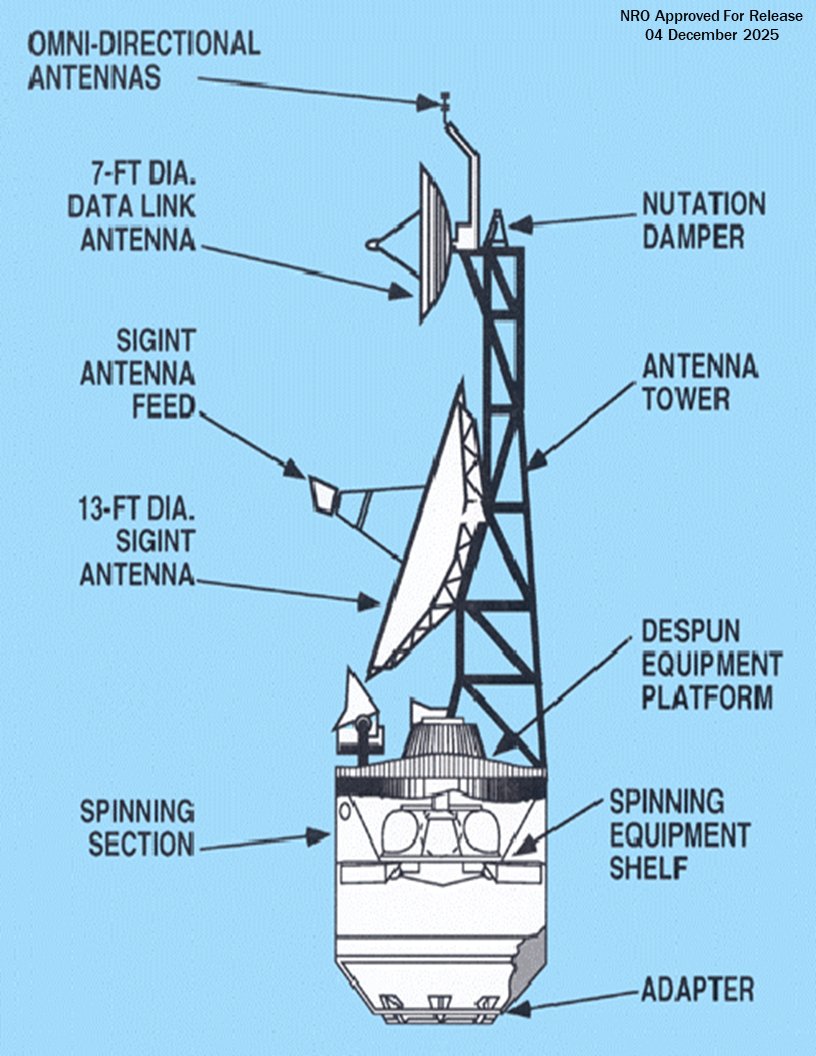
“The historical significance of Jumpseat cannot be understated,” said Dr. James Outzen, NRO director of the Center for the Study of National Reconnaissance, in a statement from the office. “Its orbit provided the United States a new vantage point for the collection of unique and critical signals intelligence from space.”
Jumpseat came as a follow-on to earlier electronic surveillance satellites, including Grab, Poppy, and Parcae.
These had begun to be fielded as the deepening Cold War heralded the possibility of a future weapons threat from space. This is something that was hammered home by the Soviet Union’s successful launch of the Sputnik 1 satellite, which would soon be followed by the first generation of ICBMs based on the same rocket technology.

“Following the end of World War II, threats of globally spreading communism and nuclear weapons proliferation fueled Americans’ anxiety of the unknown,” the NRO explains. “Across the world, the United States suspected that more American adversaries were building out extensive, topline defense arsenals including long-range missiles and atomic weapons.”
“Jumpseat’s core mission focus was to monitor adversarial offensive and defensive weapon system development,” the NRO states. “From its further orbital position, it aimed to collect data that might offer unique insight into existing and emerging threats.”
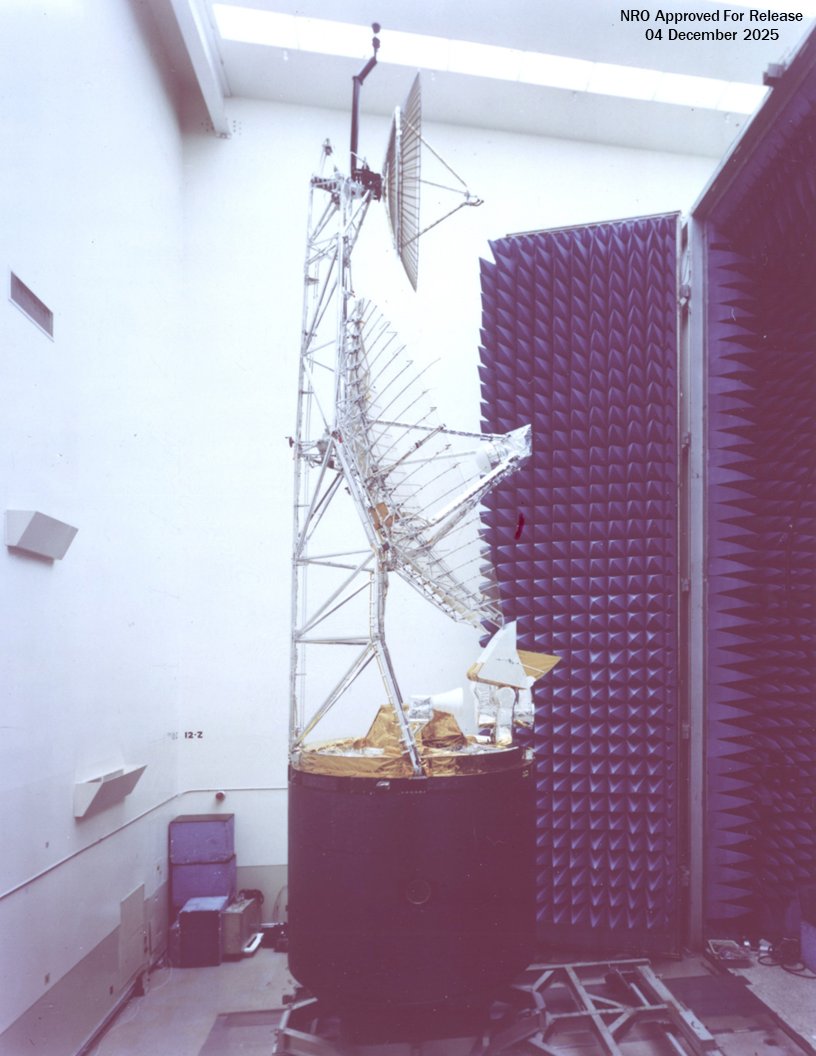

Jumpseat operated in a transponder mode, sending downlinked data to the NRO for initial processing. Once processed, the data was provided to the Department of Defense, the National Security Agency, and other national security elements.
While the NRO’s first electronic surveillance satellites — like Grab, Poppy, and Parcae —operated in low-earth orbit, Program A was tasked with developing a satellite for signals collection from a highly elliptical orbit. This was known as Project Earpop.
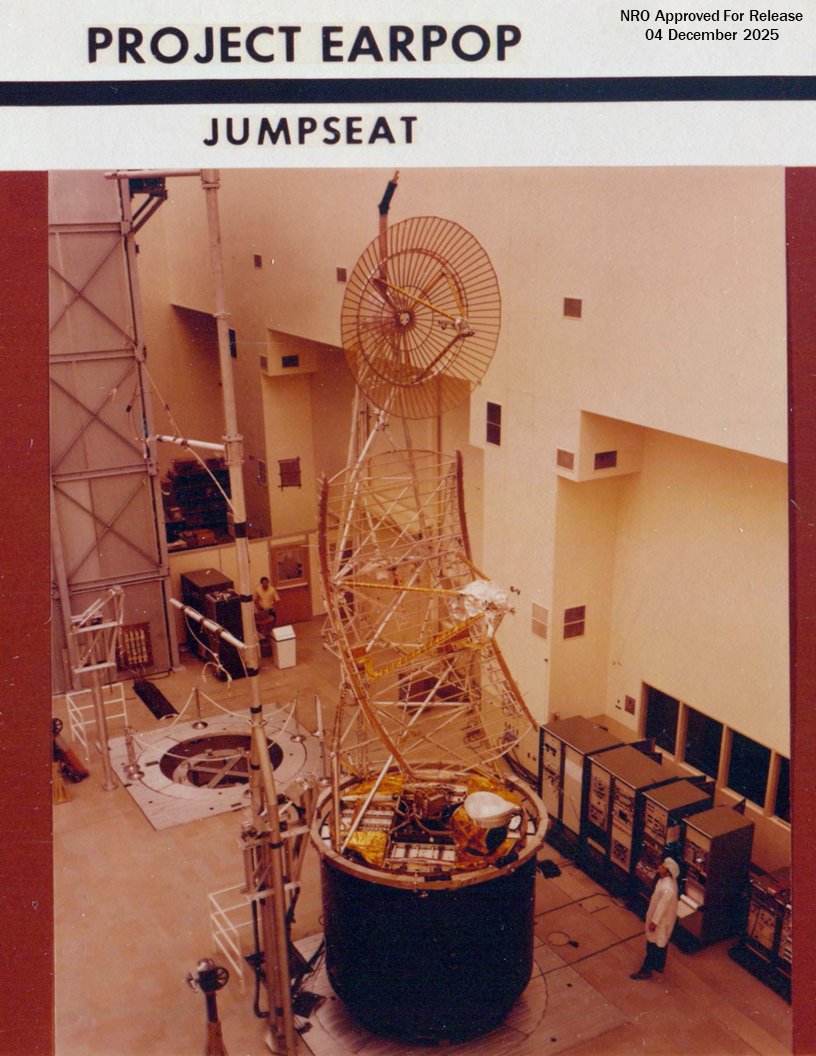

Jumpseat emerged from Earpop as “the United States’ first-generation, highly elliptical orbit (HEO) signals-collection satellite.” HEO refers to an elongated, egg-shaped trajectory, which is especially relevant for a spy satellite. In this way, the satellite has significant ‘dwell time’ at two points of its orbit, as it ascends and descends to its apogee.
In Jumpseat’s case, HEO kept the satellite for longer periods at high altitude over the northern polar regions: ideal for keeping watch on the Soviet Union. HEO above the northern polar regions is sometimes known as a Molniya orbit, after a series of Soviet satellites that operated here.
HEO, in this instance, should not be confused with a high-Earth orbit (HEO), one that takes a spacecraft beyond the geostationary orbital belt, which is defined as being around 22,236 miles above sea level.
Unconfirmed reports suggest that one of the key missions of Jumpseat was to monitor Soviet ballistic missile warning radars in the far north of the country. That would certainly make sense based on orbits, although there were plenty of other military emitters of great interest to the United States and its allies in this region.

The Jumpseat declassification memorandum notes that the satellites “performed admirably” and were only removed from the NRO’s SIGINT architecture as late as 2006.
The NRO says that the partial declassification of Jumpseat now is justified since these “will not cause harm to our current and future satellite systems.” The office also notes that it wants to bring attention to the program for its pioneering role in HEO signals-collection satellites.
As to what kinds of capabilities have taken over from Jumpseat, most aspects of these remain as secretive as their predecessor once was.
There are various unverified reports that a series of satellites known as Trumpet have taken over from Jumpseat. There are, meanwhile, many other large, classified payloads that the NRO has launched into space and which could perform similar functions
Meanwhile, this area of intelligence collection is increasingly being farmed out to commercial enterprises.
As the NRO states, “overhead collection of signals is no longer a government-only endeavor as several unclassified commercial ventures have launched signal collection systems whose capabilities are comparable if not superior to Jumpseat.”
As we have discussed in the past, the commercial space sector has opened up the possibility of constellations featuring potentially hundreds of intelligence-gathering satellites, and it will herald another revolution in both tactical and strategic space-based sensing. Starlink-like constellations, but used for sensing — which the United States is already pursuing — would be able to provide persistent surveillance of the entire globe at any given time. This would allow for continuous surveillance of any spot on the planet, not just snapshots in time taken during orbital flyovers by individual satellites. It is by no means clear what types of electronic intelligence collection can be done by such a constellation due to the small individual antenna sizes on each satellite, but if those limitations can be overcome, it could change how and when the U.S. monitors the electronic emissions of its adversaries.

Regardless, having more satellites available and having ways to rapidly deploy new systems into orbit are increasingly urgent priorities, considering the stated level of threat posed to them by Russia and, increasingly, China.
Whatever is out there, or is set to be out there in the future, it will be indebted to the trailblazing work done by the secretive Jumpseat program.
Contact the author: thomas@thewarzone.com