The U.S. Air Force has dramatically plussed-up contracts with General Electric and Pratt & Whitney, both of which now have a ceiling of $3.5 billion, to continue work on prototype next-generation jet engines. To date, the Next Generation Adaptive Propulsion (NGAP) program has been focused primarily on developing new engines to power a new sixth-generation crewed stealth ‘fighter’ in the works as part of the Next Generation Air Dominance (NGAD) initiative. The NGAD combat jet’s future is now an open question, but NGAP might also feed into other advanced aviation programs.
The Pentagon announced the modifications to the existing NGAP deals in its daily contracting notice today. Both are described as funding additional “technology maturation and risk reduction services” in support of work on prototype engines.

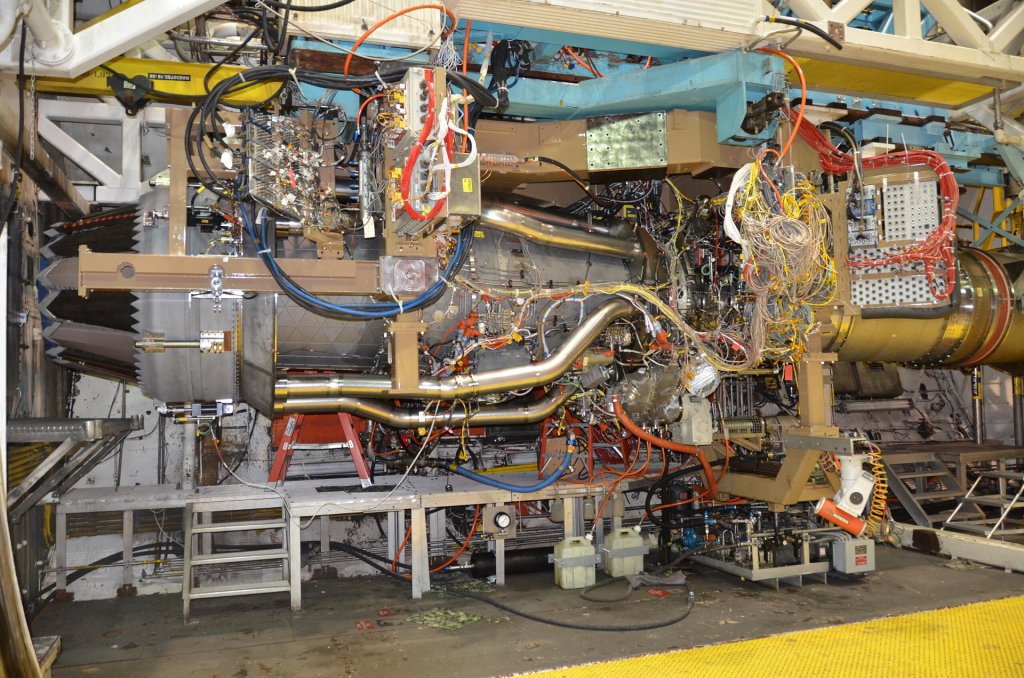
The specific entry for the modification to the NGAP contract with Pratt & Whitney (a subsidiary of Raytheon) provides the following additional context:
“The work includes design, analysis, rig testing, prototype engine build and testing, and weapon system integration. The contract modification is for the execution of the prototype phase of the Next Generation Adaptive Propulsion program and is focused on delivering a state-of-the-art propulsion system with a flexible architecture that can be tailored for future combat aircraft operating across various mission threads; and digitally transforming the propulsion industrial base.”

The U.S. Air Force first awarded the NGAP contracts to General Electric and Pratt & Whitney in 2022. At that time, additional NGAP contracts also went to Boeing, Lockheed Martin, and Northrop Grumman, the three prime contractors vying at that point to develop the NGAD combat jet, to help ensure the next-generation engines would be compatible with their respective designs. Each of those deals had an initial ceiling of close to $1 billion.
Details about the NGAP designs from General Electric and Pratt & Whitney, known as the XA102 and XA103, respectively, remain limited. The XA102 passed a major design review in 2023 and the XA103 did the same last year. They both leverage work on earlier engines that the two companies developed as potential options for re-engining F-35 Joint Strike Fighters as part of the Air Force’s Adaptive Engine Transition Program (AETP). In 2023, the Air Force announced its intention to cancel AETP in favor of upgrading the existing Pratt & Whitney F135 engine currently used on all variants of the F-35. Congress subsequently authorized additional funding for AETP.
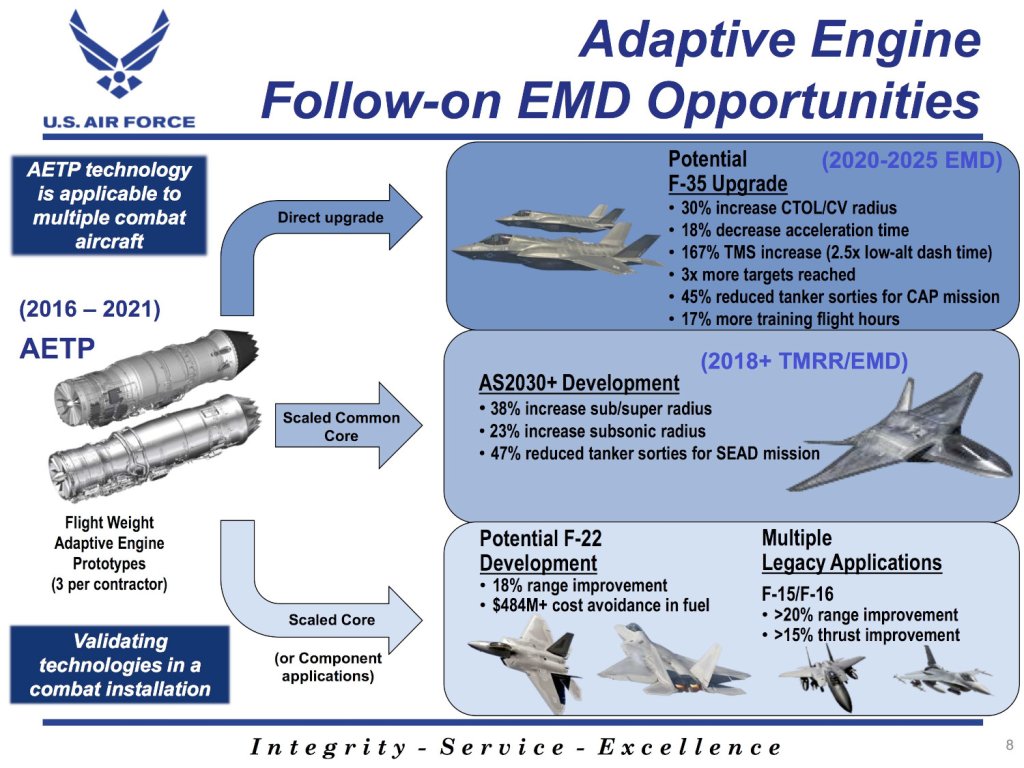
Like the XA100 and XA101, the XA102 and XA103 are known to be so-called adaptive cycle designs. What this means in broad strokes is that their bypass ratios can be adjusted on demand while in flight between modes that are more fuel-efficient or provide more power, depending on what the situation requires. For instance, a tactical jet with such an engine could fly in an ‘efficiency’ mode to an operating area, helping to conserve fuel for when it gets on station, which might include time in a higher-power combat-focused mode. The capabilities adaptive cycle engines offer could be particularly important in a future large-scale conflict, especially one against China across the board expanses of the Pacific, where aerial refueling assets are expected to be increasingly at risk and available bases could be few and far between.
General Electric has previously said that its earlier XA100 design is some 25 percent more efficient than the F135 and can also offer between 10 and 20 percent more thrust than the Pratt & Whitney engine in certain flight profiles. You can read more about the XA100 and adaptive cycle technologies here.

Despite the new funding, what any future NGAP engine might power is less clear than it was back in 2022. The Air Force launched a deep review of its NGAD combat jet plans last year and it remains unclear how the service under the new Trump administration will proceed. A number of alternatives to the original concept, envisioned as a relatively large and expensive successor to the F-22 Raptor stealth fighter but with an overall different mission set, have been proposed, including a truncated lower-cost design viewed more as a follow-on to the F-35 with a focus on acting as an aerial drone controller.
NGAP engines, or derivatives thereof, could still power the NGAD combat jet regardless of its final form. Members of a next-generation family of jet engines, or technologies therefrom, could find their way into other advanced Air Force crewed and uncrewed aircraft, as well. The service is actively working to acquire new Collaborative Combat Aircraft (CCA) drones and is also eyeing stealthy aerial refueling tankers, though the future of those efforts has also been called into question primarily due to concerns about affordability. The Air Force’s budget outlook is complicated by a number of very high-priority, but also very expensive programs, including the B-21 Raider stealth bomber and LGM-35A Sentinel intercontinental ballistic missile. The ballooning cost of Sentinel was a key factor in the decision to initiate the NGAD combat jet review.
Other branches of the U.S. military could be interested in the NGAP engines or related designs. While the future of the NGAD combat jet is murky, the U.S. Navy has insisted that it will push ahead with its own plans for a sixth-generation carrier-capable stealth ‘fighter’ commonly referred to now as F/A-XX. At the same time, in an interview with Aviation Week last year, the Navy did say it was looking to chart a course for F/A-XX independent of Air Force efforts, including NGAP.

At the same time, any engines that might come out of NGAP still look to be a ways off. The contract modifications announced today for the ongoing prototyping effort now cover work through 2032.
Whatever ultimately comes of NGAP, the expanded deals with General Electric and Pratt & Whitney show the Air Force is still very committed now to seeing the development of the XA102 and XA103 through to at least the prototype stage.
Contact the author: joe@twz.com