A North Korean drone last week entered a no-fly zone around the office of the South Korean president, military officials in Seoul have confirmed. The North Korean unmanned aerial vehicle was one of five that crossed the border on December 26, in the first incident of its kind in five years, which you can read about in our previous coverage here. While various South Korean military aircraft were scrambled to intercept the drones, none were shot down, leading to growing criticism about the ability of Seoul’s air defenses to tackle these kinds of threats.
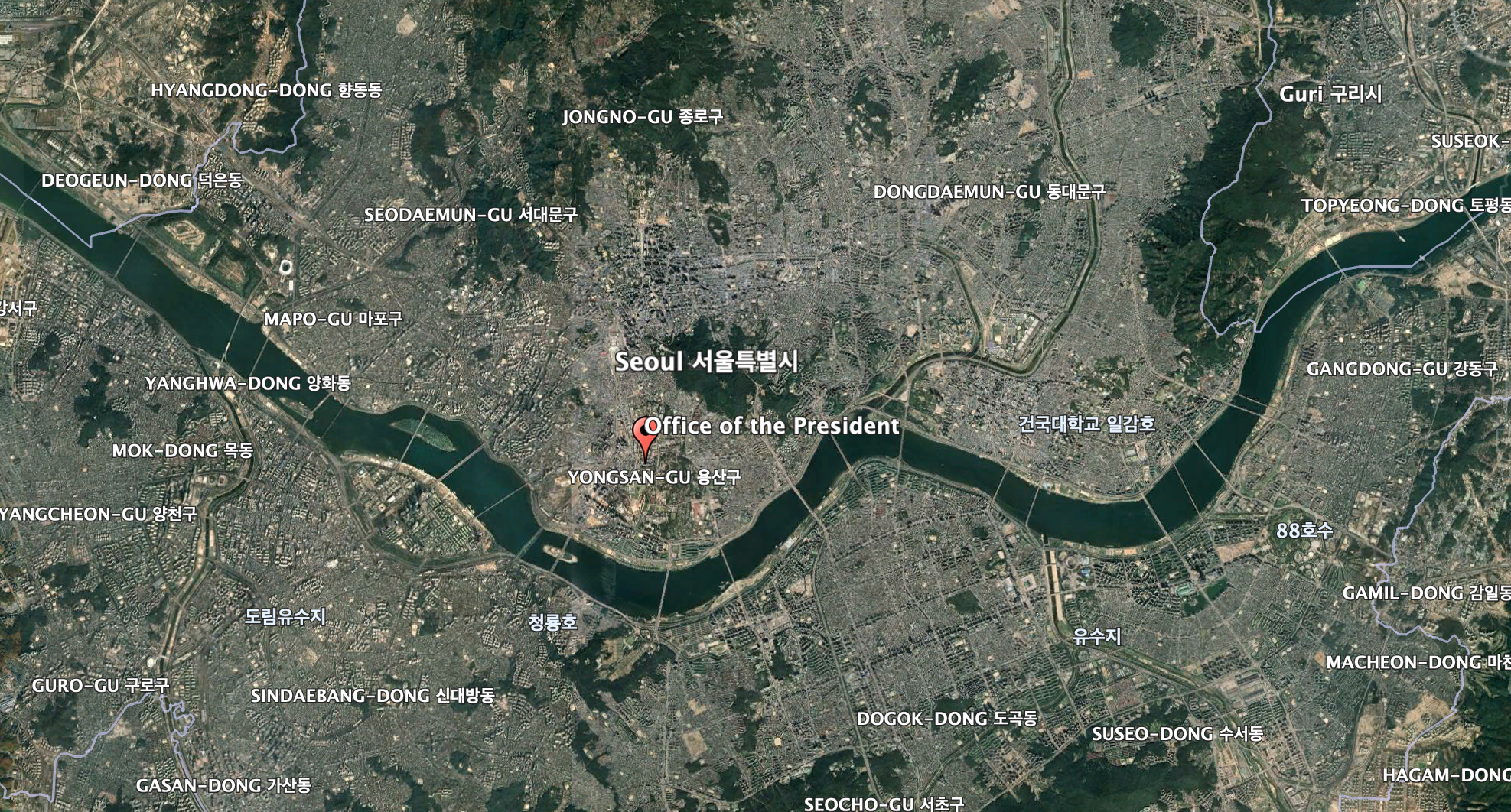
The South Korean military today revealed that one of those North Korean drones penetrated as far as a no-fly zone with a 2.3-mile radius that exists around the presidential office in the capital, Seoul. According to reports, the drone, type undisclosed, “briefly” violated the northern part of the no-fly zone, also known as zone P-73.

This contradicts previous claims from South Korea’s Joint Chiefs of Staff (JCS), which had denied that such an incident happened.
The JCS now admit that their position has changed, based on further analysis of the situation and the military’s readiness posture. However, the JCS also says that the drone didn’t directly overfly the office of President Yoon Suk Yeol, in Seoul’s Yongsan district.

An incursion by several “unknown objects” on December 26 was detected by the South Korean military before 10:30 A.M. Seoul time.
“The vehicles flew across the Military Demarcation Line separating the two Koreas and were spotted flying in those areas in Gimpo, Ganghwa Island, and Paju, leading to [the] temporary suspensions of civilian flights,” according to South Korea’s Yonhap News Agency.
The JCS confirmed the same day that one of the five drones had traveled as far as the northern part of the South Korean capital region — this presumably being the one that got within close proximity of the presidential office.
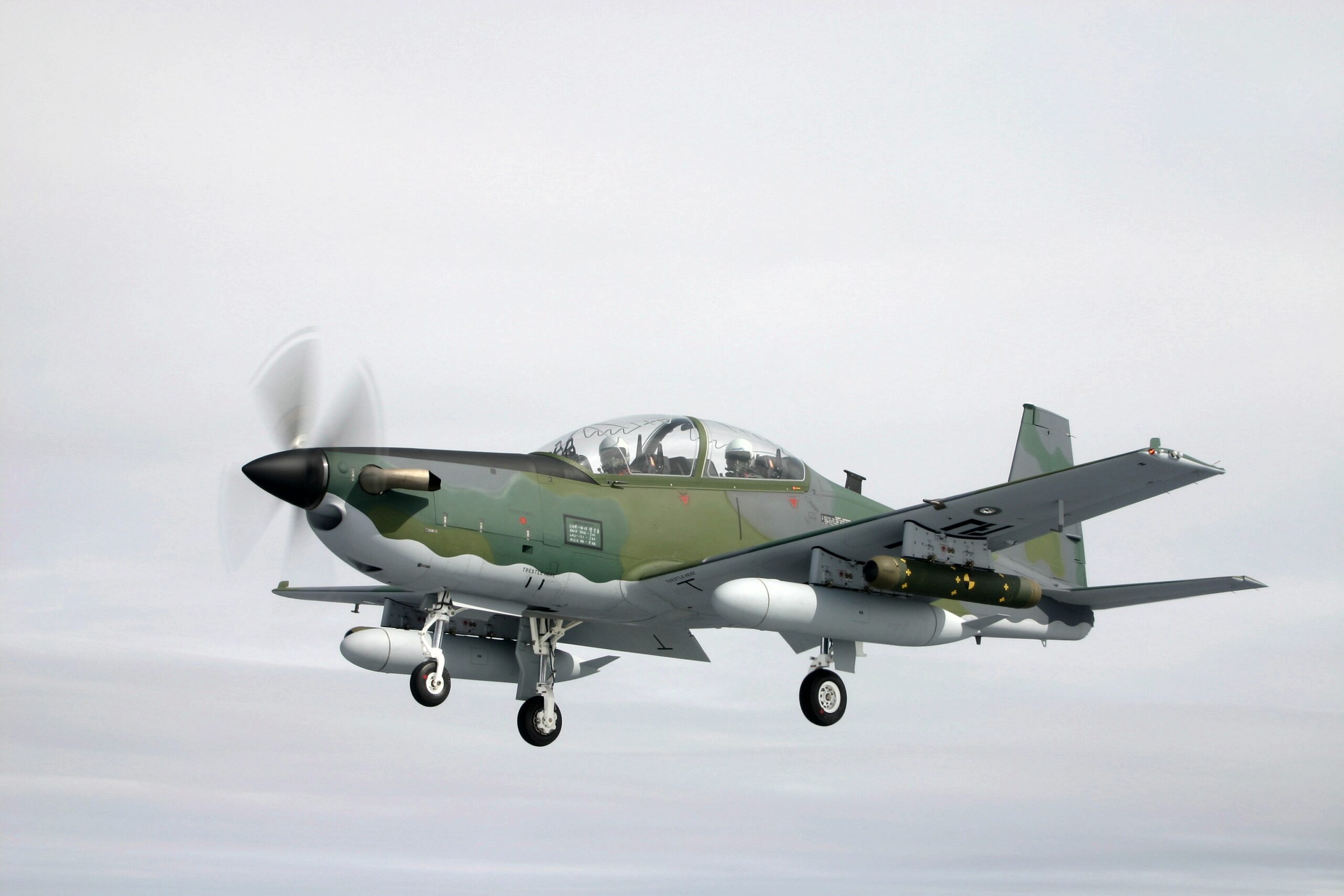
In response, the South Korean military scrambled fighter jets, turboprop light attack aircraft, and attack helicopters and fired “warning shots,” according to AP. “The attack helicopters fired a combined 100 rounds, but it wasn’t immediately known if the North Korean drones were shot down. There were no immediate reports of civilian damage on the ground in South Korea, according to the Defense Ministry.”
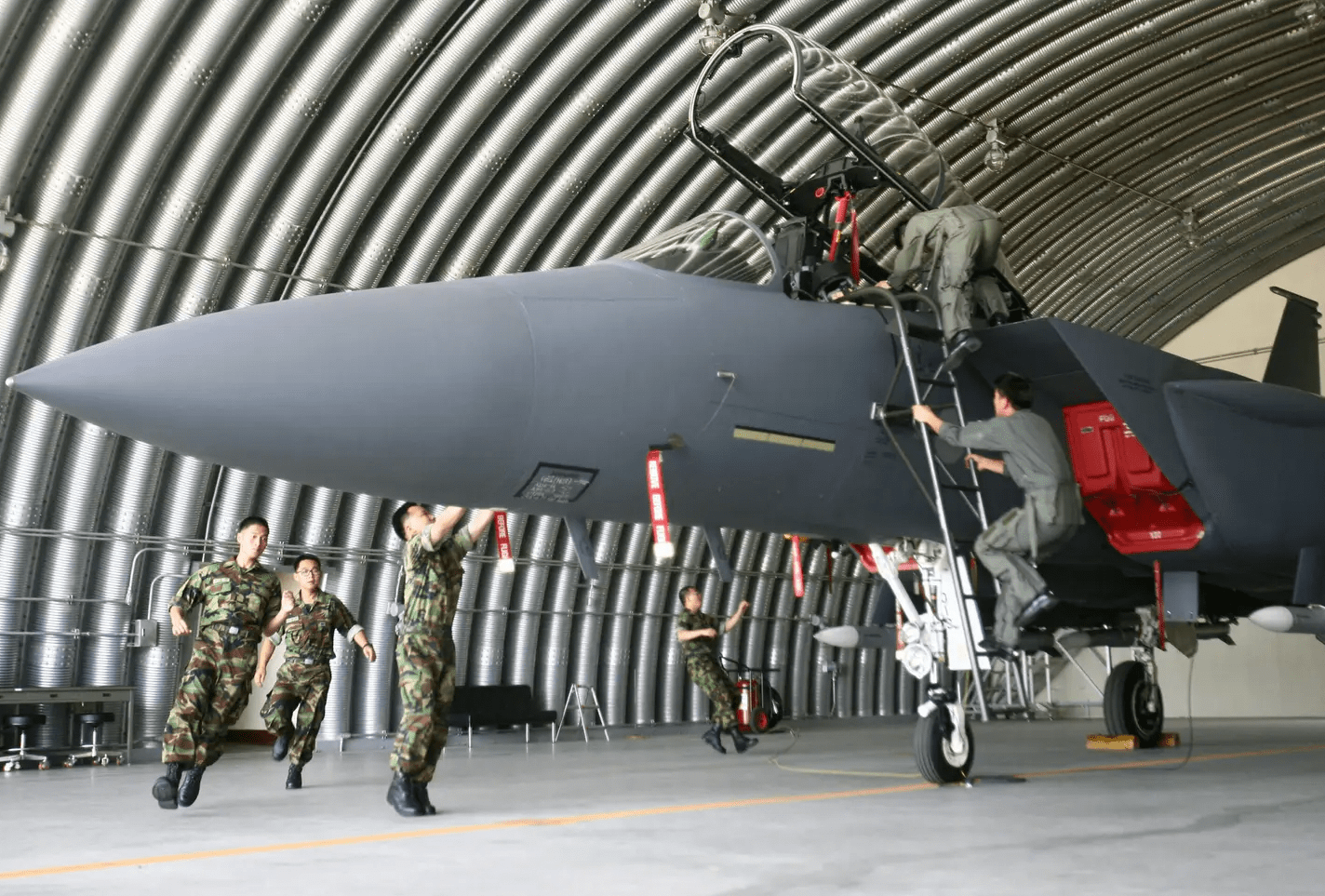

One of the KA-1 turboprop light attack aircraft that was scrambled in response was lost in a crash on takeoff, with both crew members ejecting safely.
The ability of a handful of likely fairly small North Korean drones to cause havoc amid the South Korean military is clearly a cause for some alarm, especially bearing in mind the current levels of tension on the peninsula. At this stage, however, we know little about the types of drones used or their capabilities.
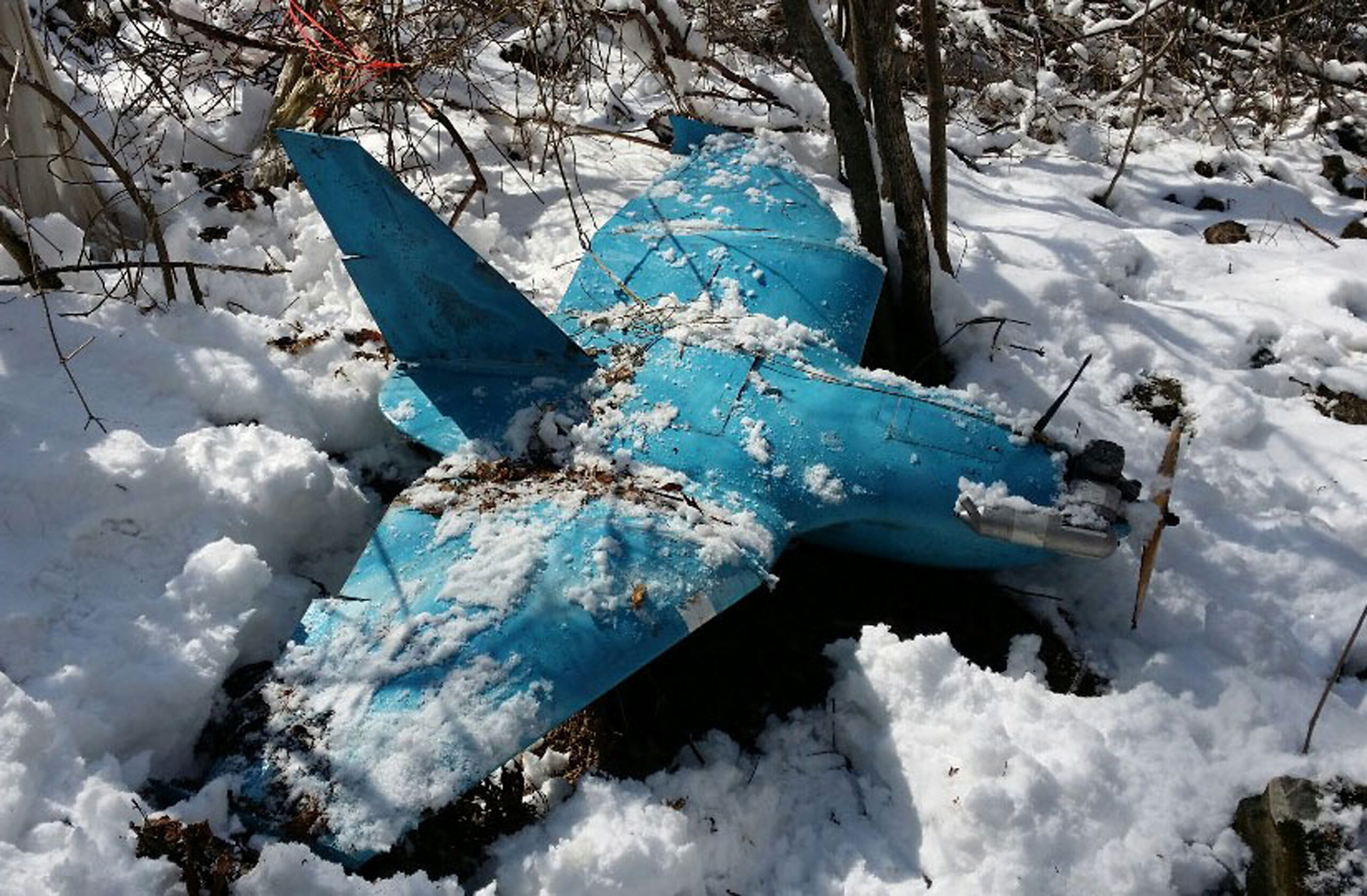

“Given the distance, altitude, and the enemy’s capabilities, we believe it was not able to take photos at that time,” an unnamed South Korean military official told Yonhap.
However, Yoo Sang-bum, a member of South Korea’s parliamentary intelligence committee, has said that, even without a direct overflight, it’s possible that the drone that penetrated into Seoul could have been used for surveillance of the presidential compound, which also includes the JCS headquarters.
Perhaps more alarming is the possibility that, in different circumstances, the drone could also have been used to carry explosives or another kind of lethal payload. Yoo also noted that North Korea does have ‘kamikaze drones’ of the kind that transport a warhead as part of a one-way mission. The idea of a strike launched by one of the Koreas to ‘decapitate’ the enemy regime is already built into war planning and drones have in the past been used to attempt to assassinate world leaders, as you can read about here.
Video showing a drone-launched assassination attempt on Venezuelan President Nicolas Maduro in the capital of Caracas in 2018:

“Our military will thoroughly and resolutely respond to this kind of North Korean provocation,” Maj. Gen. Lee Seung-o, director of operations at the South Korean JCS, told reporters at the time of the incident.
These words now ring especially hollow given today’s disclosure.
The day after the drone incursion, President Yoon slammed the military for its failure to bring down any of the drones.

“The incident showed a substantial lack of our military’s preparedness and training for the past several years, and clearly confirmed the need for more intense readiness and training,” Yoon said at a cabinet meeting.
He also called for an acceleration of work to establish a specialist military counter-drone unit, with a particular focus on smaller UAVs.
In his New Year’s address, President Yoon also called upon military commanders to punish any further North Korean provocations without fail with a “firm determination not to avoid going to war.”
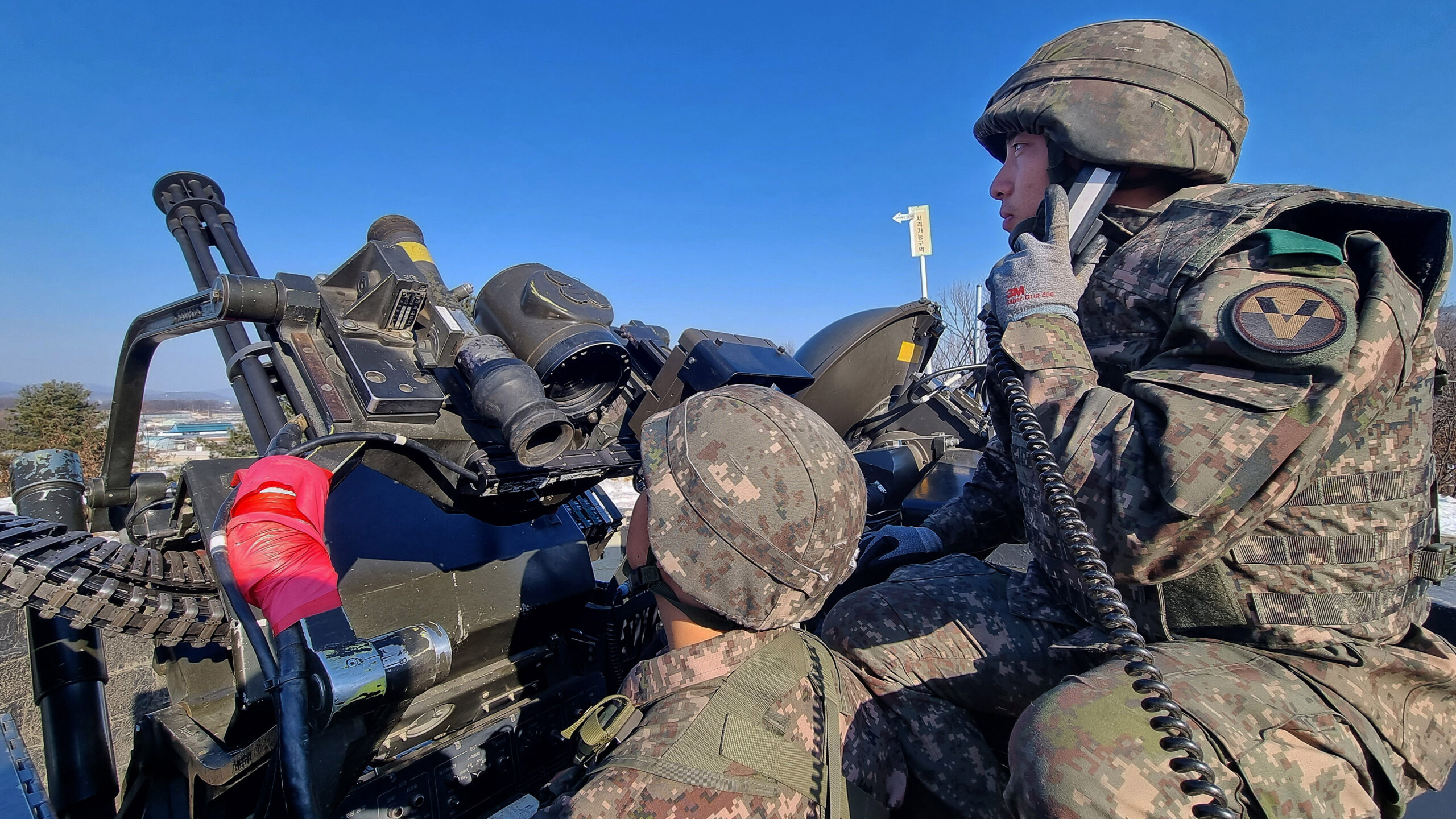
The South Korean military, too, has recently announced its plans to invest $441 million over the next five years to improve its anti-drone capabilities, including developing airborne laser weapons and signal jammers. In the meantime, the armed forces have stepped up training against drone threats, with reports of a live-fire drill today that involved some 50 aircraft, including KA-1s and MD500 helicopters, as well as soldiers armed with anti-drone jammer guns.

The North Korean drone threat is by no means new and South Korean officials are already well aware of the potential scale of UAV operations that its adversary could launch.
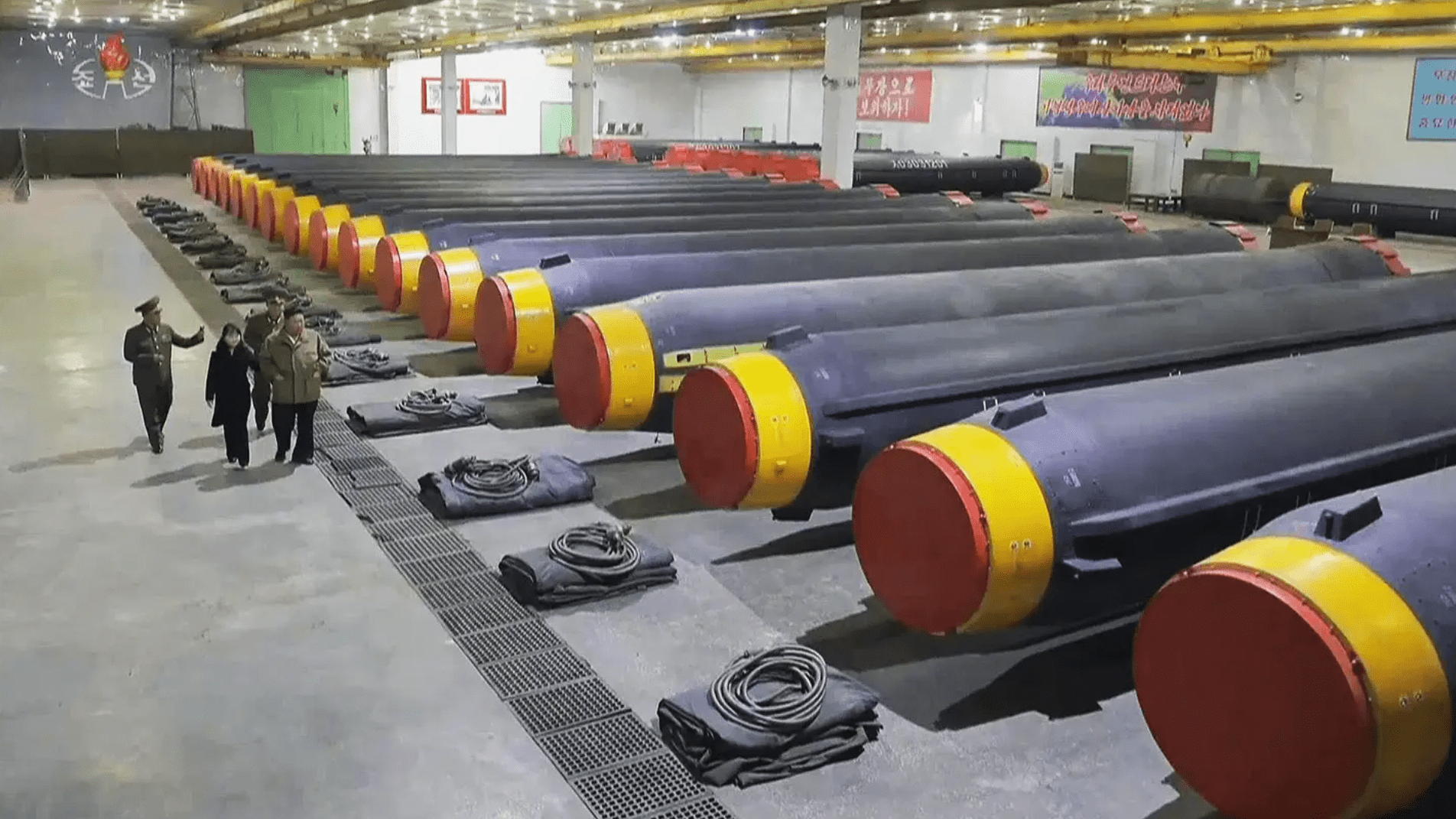
According to Yoo Sang-bum of the parliamentary intelligence committee, North Korea operates around 500 drones of some 20 different types, ranging in size from around 3-20 feet.
“A movement of developing medium- and large-sized drones for long-distance reconnaissance has been detected but it appears to be at an early stage and securing technologies such as high-performance detection sensors would be key,” Yoo said, in a report from Reuters.
As well as the mainly small and crude reconnaissance drones that are known to make up the bulk of the North’s UAV arsenal, the country also does have access to larger types, which would be able to carry more significant payloads and offer greater performance all-round. There is also evidence that North Korea has worked to clone Chinese designs, which opens up the possibility of it fielding far more capable designs, including those using ‘man-in-the-loop’ guidance and advanced sensors.
In the wake of the December 26 incursion, however, it seems likely that smaller and less complex drones are equally — if not more of — a headache for South Korea’s military. Soon after the incursion, one South Korean official compared the problem of downing a small drone to “catch[ing] a fly with cannon balls.”
The difficulty of tackling drones like this, whether weaponized or otherwise, is something we have explored on multiple occasions in the past, including in the context of various Israeli operations, the Houthi-Saudi Arabian conflict, and the war in Ukraine, where Iranian-made Shahed-136 drones and Ukraine’s own weaponized UAVs have played a prominent role. With their small radar and infrared signatures, as well as their low-altitude flight profiles, and especially their slow speed, detecting and then successfully engaging these kinds of targets is far from easy. This is especially true in the Korean example, which appears to involve drones flying on a pre-planned route and producing no radio-frequency emissions. We have highlighted this reality for years and the truth is the best air defense systems on the planet will normally have a hard time defeating this kind of threat.

The extent of the diplomatic fallout of the drone incursion is unclear but is only likely to be exacerbated by the disclosure of one of Pyongyang’s UAVs flying in close proximity to President Yoon’s office.
Already, Yoon had threatened to suspend a 2018 inter-Korean military pact if the North violates its airspace again. This pact covered calls for an end to “all hostile acts,” establishing a no-fly zone around the joint border and removing landmines and guard posts from the Demilitarized Zone.

At a time of already heightened tensions between North and South Korea, Pyongyang’s demonstration of its ability to operate drones apparently unhindered in South Korean airspace is highly notable.
Drones would almost certainly be an important part of the opening stages of any kind of conflict between the two countries, and the December 26 incident provides just a small indication of the kind of overwhelming and layered chaos that the North could unleash, even without necessarily having access to the most advanced kinds of military technologies.

While ballistic missile launches from North Korea have become fairly routine in the last year or so, and have also become more provocative, it shouldn’t be at all surprising if we now see Pyongyang also use drones as a means of signaling its intent and its willingness to test the South’s boundaries in ‘gray zone’ operations that fall short of open conflict. At the same time, it seems inevitable that North Korea is also keeping a close eye on drone operations in Ukraine, especially the effects of the Iranian-supplied Shaheds, and will likely pursue a similar capability, which is within its technological means.
For now, however, the fact that North Korea has shown itself able to fly a drone so close to the seat of political power in Seoul has understandably raised questions about how South Korea’s military would respond to more significant threats. At the same time, it also appears to be the case that Seoul’s focus on countering the North’s growing nuclear and missile arsenal means it has taken its eye off the ball somewhat when it comes to more ‘primitive’ threats like drones.
Contact the author: thomas@thewarzone.com
